 |
 |

Echinacea Root Extracts for the Prevention of Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
A Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Randomized Trial
Dieter Melchart, MD;
Ellen Walther;
Klaus Linde, MD;
Roland Brandmaier, MD;
Christian Lersch, MD, PhD
Arch Fam Med. 1998;7:541-545.
ABSTRACT
Objective To investigate the safety and efficacy of 2 extracts of echinacea for preventing upper respiratory tract infections.
Design Three-armed, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Setting Four military institutions and 1 industrial plant.
Participants Three hundred two volunteers without acute illness at time of enrollment.
Interventions Ethanolic extract from Echinacea purpurea roots, Echinacea angustifolia roots, or placebo, given orally for 12 weeks.
Main Outcome Measure Time until the first upper respiratory tract infection (time to event). Secondary outcome measures were the number of participants with at least 1 infection, global assessment, and adverse effects.
Results The time until occurrence of the first upper respiratory tract infection was 66 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 61-72 days) in the E angustifolia group, 69 days (95% CI, 64-74 days) in the E purpurea group, and 65 days (95% CI, 59-70 days) in the placebo group (P = .49). In the placebo group, 36.7% had an infection. In the treatment groups, 32.0% in the E angustifolia group (relative risk compared with placebo, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.59-1.30) and 29.3% in the E purpurea group (relative risk compared with placebo, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.53-1.31) had an infection. Participants in the treatment groups believed that they had more benefit from the medication than those in the placebo group (P = .04). Adverse effects were reported by 18 subjects in the E angustifolia group, 10 in the E purpurea group, and 11 in the placebo group.
Conclusion In this study a prophylactic effect of the investigated echinacea extracts could not be shown. However, based on the results of this and 2 other studies, one could speculate that there might be an effect of echinacea products in the order of magnitude of 10% to 20% relative risk reduction. Future studies with much larger sample sizes would be needed to prove this effect.
INTRODUCTION
HERBAL MEDICINES have widespread use all over the world. It has been estimated that in 1994, Europe spent $6 billion, Japan spent $2.1 billion, and the United States and Canada spent $1.5 billion on herbal medicine.1 One of the most popular medicinal plants is echinacea (family Compositae). The use of echinacea goes back to the North American Indians, who used it both topically and in systemic administration for ailments such as burns, snakebites, pain, cough, and sore throat.2 Nowdays, echinacea is most often used for treating and preventing uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infections such as the common cold.
Most people, including many physicians, are not aware that products commonly summarized under the name echinacea can be chemically completely different preparations. This is due to (1) the use of 3 different species of echinacea (Echinacea purpurea, Echinacea pallida, and Echinacea angustifolia); (2) the use of different plant parts (herb, roots, or both); (3) different methods of extraction (pressed juice, alcoholic extraction); and (4) the addition of other plant extracts. Depending on these factors, echinacea products can contain highly variable amounts of a variety of bioactive ingredients including caffeic acids, alkamids, polysaccharides, and glycoproteins.3 While several studies have shown in vitro and in vivo effects on immunological parameters,3 a clear mechanism of action or a single active principle has not been identified so far.
Despite widespread use, the efficacy of echinacea products is controversial.4 In Germany the evaluation committee for herbal products at the former German Federal Institute for Drugs, the Commission E, has published positive assessments for 2 echinacea preparations, E purpurea herb and E pallida root, while the evidence for other extracts was seen as insufficient.5 Data on which these assessments are based are not fully accessible. A systematic review in 1994 identified a total of 26 controlled clinical trials.6 Overall there seemed to be some evidence that echinacea products can be effective for immunomodulation, but the quality of most of the available trials was insufficient.
Unspecific upper respiratory tract infections (common cold) are a major source of morbidity worldwide and additional effective methods for their prevention and treatment would be valuable. In Germany the use of echinacea products for these purposes is widespread.7 Three randomized trials have been previously published that investigated the preventative action of 3 different echinacea products (2 of them combinations with other plant extracts).8-10 One of the trials had found a statistically significant effect over placebo,8 1 found a trend,9 and 1 had a nonsignificant result.10 Our objective was to investigate if 2 extracts from the roots of E angustifolia and E purpurea, which form part of a variety of products that are marketed in Germany but have not been subjected to randomized clinical trials, are more effective than placebo in the prevention of upper respiratory tract infections in healthy volunteers.
PARTICIPANTS AND METHODS
DESIGN
The study was randomized (stratified for participants with up to 3 and more than 3 colds in the last year; computer-generated randomization list, block size 15; concealment by consecutively numbered medication), double-blind, and placebo-controlled. The study was approved by the local ethics committee and performed according to the guidelines for good clinical practice in the European Union.
SETTING AND RECRUITMENT
The study was performed at 4 military sites (1 university, 1 health service school, and 2 regular military bases) and 1 industrial plant in and around the city of Munich, Germany. Information on the study was spread through posters and information events; interested persons were asked to contact the study center to arrange a date for individual information and the eligibility checkup.
PARTICIPANTS
Volunteers aged 18 to 65 years and free of acute illness at the time of enrollment and who gave written informed consent could participate. Exclusion criteria were as follows: acute respiratory tract infection or other infections within the last 7 days; serious progressive disease such as tuberculosis, multiple sclerosis, or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; systemic intake of corticosteroids, antibiotics, or immunostimulants in the previous 2 weeks; allergy to the Compositae family; and in the case of women, pregnancy. Participants were recruited in the winter of 1993-1994 (centers 1 and 2) and the winter of 1994-1995. They did not receive payment for their participation.
INTERVENTIONS
Participants were instructed to take 50 drops (about 20 µL equals 1 drop) of the trial preparation 2 times daily for 12 weeks from Monday to Friday. The trial preparation was packaged in 100-mL brown glass bottles that were filled either with ethanolic extracts (plant extract ratio 1:11 in 30% alcohol) from the roots of E angustifolia, E purpurea, or placebo (colored ethanolic solution).
EVALUATION
At the time of study enrollment subject characteristics (Table 1) were documented and the participants were asked to fill out 2 questionnaires regarding quality of life (Profile of Mood States [German version]11 and Activities of Daily Living12). Subjects who reported more than 3 upper respiratory tract infections in the previous 12 months were offered additional blood samples (obtained between 7 and 9 AM) for white blood cell counts and measurement of lymphocyte subpopulations at baseline and after 4, 8, and 12 weeks. Control visits were scheduled after 4 and 8 weeks for handing out new medication, asking about eventual infections, and monitoring compliance and adverse effects. At the final visit patients were asked if they believed that they benefited from the medication, were questioned about tolerability, and completed a second quality of life questionnaire. In the second recruitment phase (centers 3-5) a question was added in which the patients were asked whether they believed that they received the true treatment or the placebo.
|
|

|
|
Table 1. Characteristics of Participants (Intent-to-Treat Population)*
|
|
|
The participants had to contact the study physicians in case of any symptoms of an upper respiratory tract infection. The physician documented findings (regarding lymph nodes, throat, tongue, and temperature) and the symptoms reported by the patients (runny nose, cough, headache, pains in legs and arms, pain in throat or ears, shivering or sweating, well-being, and ability to perform normal activities) on a 4-step scale using a standardized form. To be classified as an upper respiratory tract infection at least 2 mild symptoms or 1 moderate symptom had to be present and the clinical picture had to fit the diagnosis according to the physician. The severity of the infection was classified subjectively by the physician as well as retrospectively based on the symptom scores. All necessary treatments had to be documented. Patients were given a symptom diary to evaluate the duration of symptoms. Participants who did not present immediately in case of an infection but reported an episode at 1 of the control visits were asked to rate the maximum intensity of their symptoms retrospectively and give the dates when the infection occurred.
SAMPLE SIZE CALCULATION
For reasons of sensitivity the time until occurrence of the first upper respiratory tract infection (time to event) was predetermined as the primary outcome measure for the statistical analysis instead of the number of patients with at least 1 infectious episode (incidence or relative risk, which were considered to be the most clinically relevant outcomes). A sample size calculation was performed using the nomogram by Day and Graham.13 Under the assumption that an infection would occur in 40% of placebo subjects and in 25% of the treatment groups, the required sample size per group was 125 (  = .05, = .05, 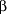 = .20). Assuming a dropout rate of about 20%, the total sample size was aimed at 450. = .20). Assuming a dropout rate of about 20%, the total sample size was aimed at 450.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Data were analyzed under blind conditions for 3 populations ("as randomized," "intent to treat," and "per protocol"; see Figure 1) using SAS (SAS Institute, Cary, NC) (for the main outcome measure; log rank test, intent-to-treat population) and SPSS (SPSS Inc, Chicago, Ill) software (all other data; Kruskal-Wallis and  2 tests for exploratory inference statistics). A predefined subgroup analysis was performed for participants who had reported more than 3 infections in the previous 12 months. 2 tests for exploratory inference statistics). A predefined subgroup analysis was performed for participants who had reported more than 3 infections in the previous 12 months.
RESULTS
A total of 302 volunteers were enrolled in the study. Seven participants only attended the enrollment date; 6 participants in 1 center dropped out of the study and the emergency envelopes with the allocation codes were broken by the local study coordinator owing to a misunderstanding. These 13 volunteers were excluded from the intent-to-treat analysis, which included 289 subjects (100 in the E angustifolia group, 99 in the E purpurea group, and 90 in the placebo group; Figure 1). A further 45 participants dropped out during the trial but were included in the intent-to-treat analysis.
At baseline there were no relevant differences between the groups (Table 1). Eighty-two percent of the subjects taking E angustifolia, 81% of those taking E purpurea, and 76% of those taking placebo reported at all control visits to have taken the medication always or almost always (<3 omissions in 4 weeks; P = .41).
A total of 113 upper respiratory tract infections occured in 96 participants; 19 infections (17%) could only be documented retrospectively. Thirty-two percent (95% confidence interval [CI], 23%-41%) of the participants in the E angustifolia group had at least 1 upper respiratory tract infection compared with 29% (95% CI, 20%-38%) in the E purpurea group and 37% (95% CI, 27%-47%) (P = .55) in the placebo group. This corresponds to a relative risk (compared with placebo) of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.59-1.30) in the E angustifolia group and 0.80 (95% CI, 0.53-1.31) in the E purpurea group.
The time until occurrence of the first upper respiratory tract infection was 66 days (95% CI, 61-72 days) among participants taking E angustifolia, 69 days (64-74 days) in the E purpurea group, and 65 days (59-70 days) in the placebo group (P = .49). The results were very similar for the randomized (P = .56) and the per protocol populations (P = .46).
There were no significant differences between the groups in the number, severity,or duration of upper respiratory tract infections (Table 2) and quality of life. Also, there was no significant difference in the time to occurrence of infections (63 vs 60 vs 57 days, P = .52), white blood cell counts, or the lymphocyte subpopulations among the subgroup of participants with more than 3 infections in the previous 12 months.
|
|

|
|
Table 2. Results (Intent-to-Treat Population)
|
|
|
More subjects in the treatment groups believed that they benefited from taking the medication (P = .04) and believed that they had been allocated to true treatment (P<.001). The proportions of subjects who correctly guessed whether they had received a true treatment or a placebo did not differ significantly between groups (P = .52).
Eighteen subjects in the E angustifolia group reported 21 adverse effects, 10 subjects in the E purpurea group reported 13 adverse effects, and 11 subjects in the placebo group reported 12 adverse effects (P = .24). None of the adverse effects were serious or required therapeutic action. Seven subjects in the E angustifolia group dropped out owing to adverse effects, compared with 2 subjects in the E purpurea group and 1 in the placebo group.
COMMENT
This study could not show that the investigated root extracts from E angustifolia and E purpurea have an effect over placebo in the prevention of upper respiratory tract infections in the population investigated. The proportions of participants developing an infection in the 2 treat-ment groups were slightly lower (corresponding to relative risk reductions of 13% for E angustifolia root and 20% for E purpurea root) than in the placebo group, but the very large CIs indicate that this could well be chance. However, 2 of the other 3 existing randomized trials on preventative effects of echinacea products yielded very similar results (15%, P = .089 and 14%, P>.110). The third available trial8 showed a much larger effect (49%, P<.05) but suffered from severe methodological shortcomings (eg, an unclear but probably large number of randomized subjects were excluded from the analysis). The heterogeneity of the investigated products precludes a sound meta-analysis of these trials. Nonetheless, we think it is plausible to recommend that any future trials of preventive effects of echinacea products should be planned to detect effect sizes of 10% to 20% relative risk reduction. If there should be a true effect in that order of magnitude, our trial was massively undersized (a power of about 20%). This situation would have changed only slightly if we had met our original aim of recruiting 450 participants; for adequate statistical power we would have had to recruit more than 1000 participants.
The most significant result in our study was observed when we asked the participants at the end of the study to guess whether they had received 1 of the 2 true treatments or placebo. Participants in the treatment groups assumed more often that they had received a true treatment than those in the placebo group. However, the rates of participants correctly guessing whether they were in the placebo or treatment group were similar in the 3 groups. These findings are difficult to interpret. There are 2 possible explanations: (1) It might be that participants in the treatment groups truly felt more subjective benefit than those in the placebo group and, therefore, assumed more often that they had received the treatment (and the opposite in the placebo group). This would mean that the treatment was more effective than placebo on a subjective level. (2) Some participants might have found out whether the treatment they received was echinacea or placebo. Because of the characteristic taste of echinacea extracts it is almost impossible to prepare a completely indistinguishable placebo.
Unblinding is rarely discussed in clinical research.14-15 There are no reliable procedures to quantify the degree of this problem in a trial. The mutual interactions between perceived efficacy, adverse effects, and guesses make an analysis difficult. In our trial the guesses of the participants were correct in about half of the cases (53%), wrong in about one quarter (22%), and another quarter of the participants felt unable to make a guess (25%). If one quarter of the participants made a wrong guess, it seems reasonable to expect that a similar proportion of participants made a correct guess just by chance. In consequence, unblinding due to 1 of the aforementioned reasons might have happened in about 30% of the participants. This casts further doubts on our findings. However, we think that it is a strength of our study that we tried to seriously deal with that problem instead of ignoring it.
While not reaching statistical significance, our data do suggest that the E angustifolia root extract might be associated with more adverse effects than the E purpurea root extract or placebo. Overall, tolerability was good in all 3 groups.
The fact that 45% of the participants reported trying an echinacea product at least once before participation in this study demonstrates its widespread use. Further research is therefore mandatory. However, at least in Germany, it seems unlikely that the resources needed for such research will be available. Echinacea products are prepared and marketed by many relatively small manufacturers who have neither the resources nor the know-how to sponsor and coordinate rigorous large-scale studies. The problem of standardization is also still not solved; consequently, it is very difficult to assess to what degree evidence on a specific product or even on a specific lot of one product can be extrapolated to others. Finally, as phytopharmaceuticals are generally licensed as extracts, patents for specific products are not provided unless the extract has unique features. The interest of a manufacturer to invest huge amounts of money in research whose results, in case of "success," can then easily be used by competitors is limited. In conclusion, we believe that clinical research on echinacea, at least in Germany, will remain underfunded. Unfortunately, performing rigorous trials without adequate funding is nearly impossible.
The relatively small effect sizes that can be expected, based on the available data in prevention trials, and the considerable costs of such studies raise the question of whether there would be other ways to perform clinical research on echinacea while making efficient use of the limited resources. A recent rigorous trial found that early treatment (when the patients only feel the very first symptoms of a cold) with high doses of the pressed juice of E purpurea herb decreased significantly the number of persons developing a "full" common cold and decreased the duration of the illness.16 Another recent trial found similar results for a mixture of E purpurea herb and root.17 This type of early treatment is widespread in self-medication and might be a more promising direction for future research.
AUTHOR INFORMATION
Accepted for publication July 10, 1998.
The Center for Complementary Medicine Research is sponsored by the Bavarian Parliament. This study was partly supported by Plantapharmazie, Göttingen, Germany.
Reprints: Dieter Melchart, MD, Center for Complementary Medicine Research, Technische Universität, Kaiserstrasse 9, 80801 Munich, Germany (e-mail: Muenchener.Modell{at}lrz.uni-muenchen.de).
From the Center for Complementary Medicine Research (Drs Melchart and Linde and Ms Walther) and Medizinische Klinik (Dr Lersch), Technische Universität; and Biometrisches Zentrum für Therapiestudien (Dr Brandmaier), Munich, Germany.
REFERENCES
1. Grünwald J, Büttel K. Der europäische Markt für Phytotherapeutika. Pharm Ind. 1996;58:209-214.
2. Bauer R, Wagner H. Echinacea: Handbuch für Ärzte, Apotheker und andere Naturwissenschaftler. Stuttgart, Germany: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft; 1990.
3. Bauer R, Wagner H. Echinacea species as potential immunostimulatory drugs. In: Wagner H. Economic and Medicinal Plant Research. London, England: Academic Press; 1991:253-321.
4. Schoenhoefer PS, Schulte-Sasse H. Sind pflanzliche Immunstimulantien wirksam und unbedenklich? Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1989;114:1804-1806.
PUBMED
5. Blumenthal M, Goldberg A, Gruenwald J, Hall T, Riggins CW, Rister RS. The German Commission E Monographs: Therapeutic Monographs on Medicinal Plants for Human Use. Klein S, Rister RS, trans. Austin, Tex: American Botanical Council; 1998.
6. Melchart D, Linde K, Worku F, Bauer R, Wagner H. Immunomodulation with echinacea: a systematic review of controlled clinical trials. Phytomedicine. 1994;1:245-254.
7. Haustein KO. Immuntherapeutika. In: Schwabe U, Paffrath D, eds. Arzneiverordnungsreport 1994. Stuttgart, Germany: Fischer; 1994:245-250.
8. Forth H, Beuscher N. Beeinflussung der Häufigkeit banaler Erkältungsinfekte durch Esberitox. Z Allgemeinmedizin. 1981;57:2272-2275.
9. Schmidt U, Albrecht M, Schenk N. Immunstimulans senkt Häufigkeit grippaler Infekte. Natur Ganzheitsmedizin. 1990;3:277-281.
10. Schöneberger D. Einfluss der immunstimulierenden Wirkung von Presssaft aus Herba Echinaceae purpureae auf Verlauf und Schweregrad von Erkältungskrankheiten. Forum Immunol. 1992;2:18-22.
11. Bullinger M, Heinisch M, Ludwig M, Geier S. Skalen zur Erfassung des Wohlbefindens: Psychometrische Analysen zum "Profile of Mood States" (POMS) und zum "Psychological General Well-Being Index" (PGWB). Z Differ Diagn Psychol. 1990;11:53-61.
12. Bullinger M, Hasford J. Evaluating quality of life measures for German clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1991;12:915-924.
13. Day SJ, Graham DF. Sample size estimation for comparing two or more treatment groups in clinical trials. Stat Med. 1991;10:33-44.
WEB OF SCIENCE
| PUBMED
14. Moscucci M, Byrne L, Weintraub M, Cox C. Blinding, unblinding, and the placebo effect: an analysis of patients' guesses of treatment assignment in a double-blind clinical trial. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1987;41:259-265.
WEB OF SCIENCE
| PUBMED
15. Byrington RP, Curb JD, Mattson ME. Assessment of double-blindness at the conclusion of the Beta-blocker Heart Attack Trial. JAMA. 1985;253:1733-1736.
FREE FULL TEXT
16. Hoheisel O, Sandberg M, Bertram S, Bulitta M, Schäfer M. Echinacea treatment shortens the course of the common cold: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur J Clin Res. 1997;9:261-269.
17. Brinkeborn R, Shah D, Geissbühler S, Degenring FH. Echinaforce zur Behandlung von akuten Erkältungen. Schweiz Zschr Ganzheitsmedizin. 1998;10:26-29.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN CITED BY OTHER ARTICLES
 |
Complementary and alternative medicine for prevention and treatment of the common cold
Nahas and Balla
cfp 2011;57:31-36.
ABSTRACT
| FULL TEXT
Echinacea purpurea Therapy for the Treatment of the Common Cold: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
Yale and Liu
Arch Intern Med 2004;164:1237-1241.
ABSTRACT
| FULL TEXT
Echinacea purpurea for Prevention of Experimental Rhinovirus Colds
Sperber et al.
Clinical Infectious Diseases 2004;38:1367-1371.
ABSTRACT
| FULL TEXT
Effectiveness of an Herbal Preparation Containing Echinacea, Propolis, and Vitamin C in Preventing Respiratory Tract Infections in Children: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter Study
Cohen et al.
Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2004;158:217-221.
ABSTRACT
| FULL TEXT
Regulation of Human Immune Gene Expression as Influenced by a Commercial Blended Echinacea Product: Preliminary Studies
Randolph et al.
Exp Biol Med 2003;228:1051-1056.
ABSTRACT
| FULL TEXT
Immune System Effects of Echinacea, Ginseng, and Astragalus: A Review
Block and Mead
Integr Cancer Ther 2003;2:247-267.
ABSTRACT
Effect of dietary Echinacea purpurea on viremia and performance in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus-infected nursery pigs
Hermann et al.
J ANIM SCI 2003;81:2139-2144.
ABSTRACT
| FULL TEXT
Treatment of the Common Cold with Unrefined Echinacea: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Barrett et al.
ANN INTERN MED 2002;137:939-946.
ABSTRACT
| FULL TEXT
The Use of Dietary Supplements in Pediatrics: A Study of Echinacea
Mark et al.
CLIN PEDIATR 2001;40:265-269.
ABSTRACT
Need for Additional, Specific Information in Studies with Echinacea
Dennehy et al.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001;45:369-370.
FULL TEXT
Pregnancy Outcome Following Gestational Exposure to Echinacea: A Prospective Controlled Study
Gallo et al.
Arch Intern Med 2000;160:3141-3143.
ABSTRACT
| FULL TEXT
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis after parenteral therapy with herbal extracts: a report of two cases
Schwarz et al.
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000;69:516-518.
ABSTRACT
| FULL TEXT
Immunopharmacological activity of Echinacea preparations following simulated digestion on murine macrophages and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Rininger et al.
J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000;68:503-510.
ABSTRACT
| FULL TEXT
Inflammation and Native American medicine: the role of botanicals
Borchers et al.
Am J Clin Nutr 2000;72:339-347.
ABSTRACT
| FULL TEXT
Ineffectiveness of Echinacea for Prevention of Experimental Rhinovirus Colds
Turner et al.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000;44:1708-1709.
ABSTRACT
| FULL TEXT
No Support for Echinacea in Preventing URIs
JWatch General 1998;1998:9-9.
FULL TEXT
|