
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Neurological Disease: Listening to Gene Silencers
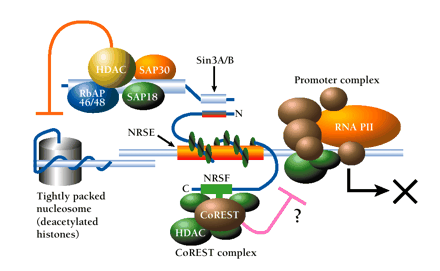
Dual mechanism of repression via the NRSF–NRSE interaction. The N-terminal domain of NRSE-bound NRSF interacts with Sin3, which in turn recruits histone deacetylase (HDAC) and associated proteins (SAP30, SAP18, RbAp46/48) to the promoter region. HDAC deacetylates lysine residues of nucleosomal core histones, which consequently limits the accessibility of DNA to transcription factors; the resulting inhibition of RNA polymerase activity (RNA PII) is indicated schematically by an X. In addition, a zinc-finger domain proximal to the C terminus of NRSF interacts with CoREST. CoREST recruits an HDAC complex that includes HDAC1 and HDAC2 and mediates repression that is distinguished by resistance to trichostatin A. Multiple corepressor mechanisms are thus indicated; see text for details.


