
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Transactivation of the EGF Receptor: Is the PDGF Receptor an Unexpected Accomplice?
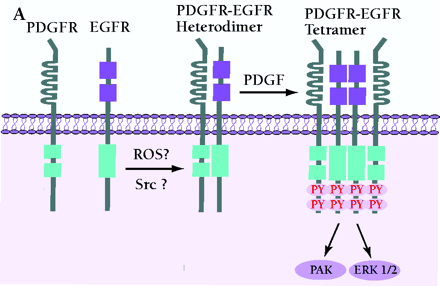
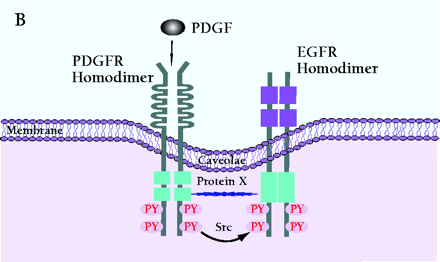
Mechanism of PDGF-induced EGFR transactivation. A. Model of basal PDGFβR-EGFR heterodimer formation and signal transduction. As proposed by Saito et al., PDGFβR-EGFR heterodimers exist in unstimulated cells (11). The formation of the heterodimer provides a scaffold for other molecules that induces EGFR transactivation and downstream signaling. The constitutive interaction between PDGFβR and EGFR is regulated by ROS and Src family kinases. B. Alternative mechanism of EGFR transactivation in caveolae. Caveolae are the principal location of PDGFβR (14). Upon PDGF binding to PDGFβR, EGFR is activated by Src-mediated phosphorylation prior to the formation of EGFR homodimers. The heterodimers between EGFR and PDGFβR may bind each other indirectly as a part of a large cross-linked complex involving unknown proteins.


