
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
GAF Domains: Two–Billion–Year–Old Molecular Switches that Bind Cyclic Nucleotides
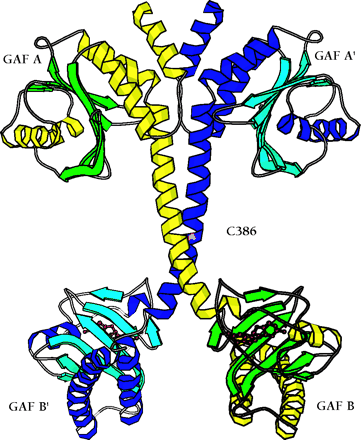
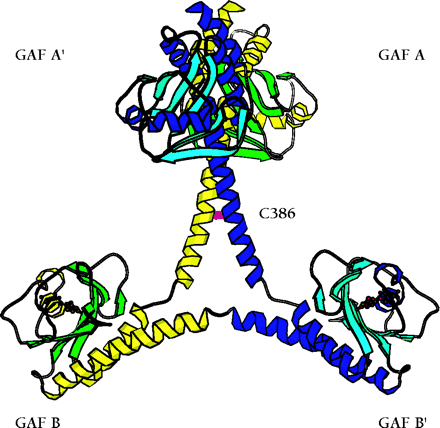
The backbone ribbon depicts the dimeric regulatory segment from PDE2A. A. The two GAF A domains interact to promote dimerization, and are adjacent to nine-turn helices that may be disulfide linked to each other at residues C386; at the C-terminal ends occur the GAF B domains that bind cGMP. B. View rotated ∼70 degrees with respect to the image in Figure 2A. Only the first seven turns of the nine-turn helices that intervene between the GAF A and GAF B sequences of each monomer are involved in dimerization. The GAF B domains are ∼65 angstroms apart. The overall dimensions of the dimerized regulatory segments are 105 by 92 by 71 angstroms. Beta sheets are colored in light blue and green; alpha helices in dark blue and yellow. Cyclic GMP is shown in red.


