
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Sex, Digitalis, and the Sodium Pump
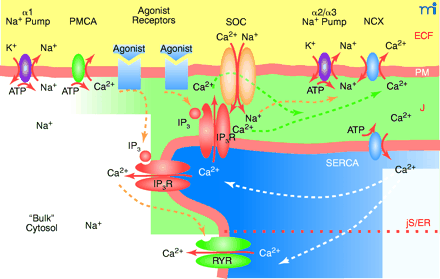
The plasma membrane-junctional sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum (PM-jS/ER) region (PLasmERosome). The important ion transporters involved in the local control of jS/ER Ca2+ stores and modulation of Ca2+ signals are shown. The PM overlying “bulk” cytosol contains Na+ pumps with α1 subunits (the “housekeeping” isoform that maintains the low, bulk cytosolic Na+ concentration) and PM Ca2+ pumps (PMCA). The PM microdomain overlying jS/ER contains Na+ pumps with α2 or α3 subunits, NCX, and store-operated channels (SOCs). α1 Na+ pumps are widely distributed in the PM but appear to be excluded from these microdomains. Agonist receptors may be expressed in these PM microdomains as well as elsewhere on the PM. The jS/ER contains S/ER Ca2+ pumps (SERCA), inositol trisphosphate receptors (IP3R) and ryanodine receptors (RYR). Although not illustrated here, the PM microdomain in some cell types (e.g., cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle) may contain L-type Ca2+ channels (dihydropyridine receptors), and the jS/ER may contain RYR. A very small, “diffusion-restricted” cytosolic space (J) lies between the PM and jS/ER; the concentrations of Na+ and Ca2+ may differ from those in bulk cytosol. Shading indicates relative concentrations of Na+ or Ca2+. The dotted orange line within the S/ER refers to the apparent compartmentalization of the S/ER in many types of cells. Only the upper compartment illustrated in the figure can be considered the junctional S/ER (jS/ER). ECF, extracellular fluid. Adapted from (45).


