
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Phosphorylation of G Protein–Coupled Receptors: GPCR Kinases in Heart Disease
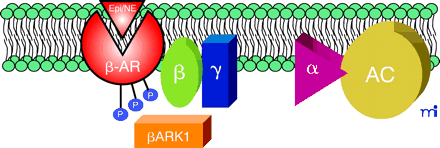
The nexus of catecholamine receptor, G protein, and GPCR kinase: An opportunity for cardiotherapeutic intervention. Schematized is a molecule of βARK1 (i.e., GRK2), the most abundant cardiac GRK, which is positioned, through the interaction between its C-terminal domain and the βγ heterodimer (Gβγ) of an activated G protein, so as to phosphorylate a βAR molecule. Phosphorylation results in cellular desensitization to catecholamines, which may be involved is certain pathological conditions. To prevent the phosphorylation of the βAR (and thereby preclude desensitization), therapeutic strategies may utilize peptides or small molecules that interfere with the interaction between GRKs and the Gβγ heterodimer.


