
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
CaMKII, an Enzyme on the Move: Regulation of Temporospatial Localization
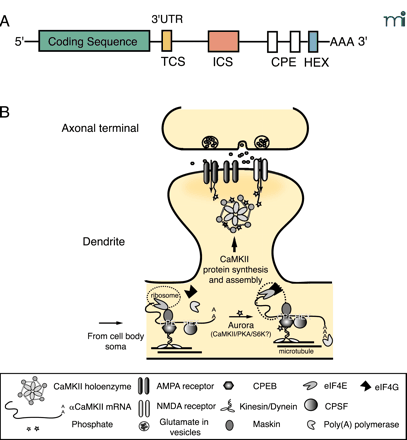
Mechanisms for dendritic targeting and translation of α CaMKII mRNA. A. The mRNA sequence structure of αCaMKII. The 3′ UTR of αCaMKII has several elements that are important for dendritic targeting. The Targeting Cis-Sequence (TCS) is a 27-nt sequence that contains a RNA transport sequence (CGCAGAGAUC) known to be necessary for the targeting of myelin basic protein mRNA in oligodendrocyte. The 648-nt Inhibitory Cis-Sequence (ICS) requires synaptic activity to override its intrinsic inhibition of dendritic targeting. There are two Cytoplasmic Polyadenylation Elements (CPEs)—UUUUUAU—in the 3′ UTR of CaMKII. The hexanucleotide (i.e., AAUAAA) polyadenylation signal (HEX) is shown. These elements can bind to trans-acting proteins, such as the CPE-binding protein CPEB, which has been implicated in facilitation of the targeting of αCaMKII mRNA (54, 59, 60). B. Regulatory mechanisms for the dendritic targeting and translation of αCaMKII mRNA. Transient synaptic activity leads to transport of αCaMKII mRNA from the soma to the base of the dendrite where transcripts associate with ribosomes through an interaction between CPE and CPEB. Motor proteins (i.e., Kinesin/Dynein) shuttle the protein–transcript complex on the microtubule network to the dendrites (61). CPEB also binds to maskin, which has an inhibitory interaction with the eukaryotic initiation factor eIF4E at the cap of αCaMKII mRNA and prevents translation until triggered by synaptic activity. Sustained synaptic activity activates Aurora—a Ser–Thr kinase whose activity might be required for local translation of dendritic mRNAs—or possibly other kinases such as PKA, CaMKII or S6 kinase to phosphorylate the different isoforms of CPEB in synapses (63, 92). Phosphorylation of CPEB triggers a conformational change that brings the HEX-binding cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor CPSF in contact with CPEB. Maskin is released from eIF4E which then recruits eIF4G for proper assembly of αCaMKII mRNA onto ribosomes. Poly(A) polymerase extends the poly-A tail and nascent CaMKII polypeptides are synthesized (92).


