
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Ubiquitination for Activation: New Directions in the NF-κB Roadmap
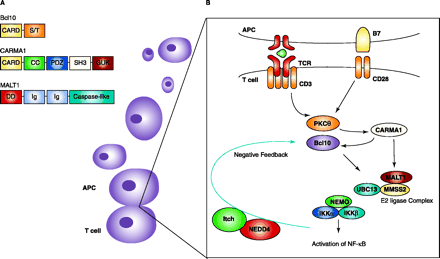
Mapping NF-κB activation in T cells. A. Domain structure of Bcl10, CARMA1, and MALT1. Domains within each protein may promote homo-oligomerization and multiprotein complex formation. CARD, caspase recruitment domain; S/T, serine-threonine-rich domain; CC, coiled-coil domain; PDZ, postsynaptic density 95, discs large, and zona occludens-1 domain; SH3, Src homology 3 domain; GUK, guanylate kinase domain; DD, death domain; Ig, immunoglobulinlike repeats; caspase-like, a domain very similar to those found in caspase proteins. B. Upon TCR activation, CARMA1 interacts with Bcl10 at the immunological synapse via their CARD domains. CARMA1 also recruits PCK??to the lipid rafts at the synapse, which may further aid Bcl10 activation. Through its coiled-coil domain, Malt1 binds CARMA1. Malt1 is, itself, recruited to the rafts. Bcl10 induces the oligomerization of Malt1, allowing for the formation of a ubiquitin-conjugating E2 complex consisting of UBC13 and MMS2. These molecules catalyze K63-linked polyubiquitination of NEMO (leading to its destruction) and the activation of IKK. Ubiquitin ligases NEDD4 and Itch can also negatively regulate this pathway by degrading Bcl10.


