
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Collateral Damage in Cancer Chemotherapy: Oxidative Stress in Nontargeted Tissues
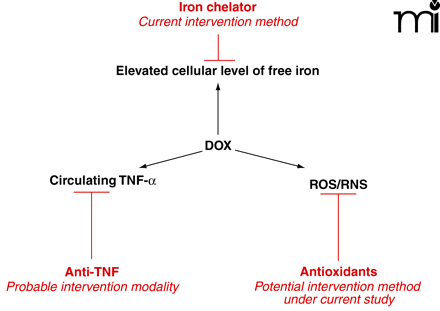
Figure 5.
Mechanism-based interventions into DOX-induced oxidative damage. Iron chelators reduce free cellular iron ions and disrupt the propagation of ROS/RNS and are thus used to reduce DOX cardiotoxicity. The efficacies of antioxidants to decrease oxidative damage in the heart and brain are now also under intensive study. Modulation of circulating TNF-α may be an intervention modality to reduce DOX-induced oxidative damage in the brain. See text for details.


