
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Regulation of Receptors and Transporters by Ubiquitination: New Insights into Surprisingly Similar Mechanisms
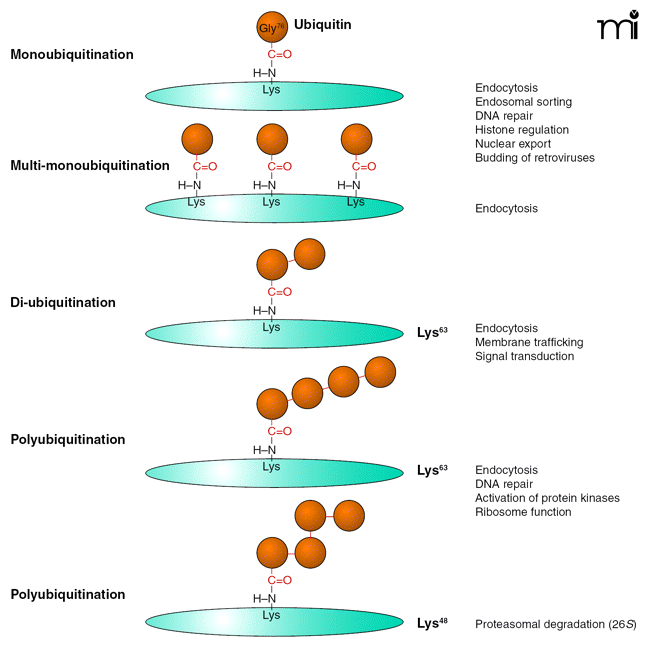
Types of ubiquitin conjugation. Gly76 of ubiquitin is covalently attached to the ε-amino group of lysines in the substrate. Substrates can be modified with a single ubiquitin molecule at a single (monoubiquitination) or multiple (multi-monoubiquitination) lysine residues. Further ubiquitin conjugation to the lysine residues of ubiquitin results in diubiquitin or polyubiquitination. Shown are the most frequently detected ubiquitin chains linked through Lys63 or Lys48 of ubiquitin. Lys48- or Lys63-linked chains have closed and extended conformation, respectively, resulting in different mechanisms of recognition by ubiquitin binding domains (UBDs).


