
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Translational NeuroImaging of the CNS: Novel Pathways to Drug Development
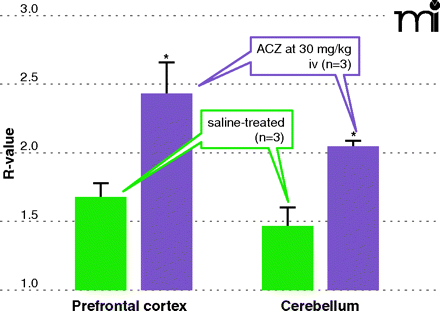
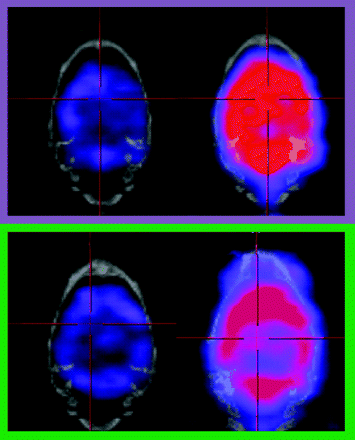
Drug-induced changes in cerebral blood flow evaluated by split-dose SPECT. In the split-dose SPECT study, rats were infused with a first dose of 99mTc-HMAPO at 1 mCi followed by a second dose at 2 mCi; changes in blood flow were then elicited by saline (n=3) or acetazolamide at 30mg/kg iv (n=3). Based on the images acquired from the pre-drug and post-drug periods, mean R-values (indicator of relative drug-induced change in cerebral blood flow) were calculated from specific regions of interest. Our results indicated that, compared to saline-treated rats, ACZ-treated rats show changes in prefrontal cortex (PFC) and cerebellum that reflect the known vasodilatation effect of ACZ. This imaging technique has been widely used in humans, and thus it can serve as a useful translational tool for drug discovery.


