 |
 |

Practice Commentary
Louis Kuritzky, MD
Arch Fam Med. 1997;6(5):506.
 |
 |
| Since this article does not have an abstract, we have provided the first 150 words of the full text PDF and any section headings. |
|
 |
 |
Given that monotherapy with any of the traditional first-line therapies for hypertension is successful in achieving target blood pressure in only about 50% of cases, primary care clinicians recognize that a substantial group of patients will require therapeutic revisions. In refractory hypertension (requiring 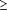 3 drugs for adequacy of control), escalation of cost and side effects necessitates flexibility in using the full gamut of therapeutic options. 3 drugs for adequacy of control), escalation of cost and side effects necessitates flexibility in using the full gamut of therapeutic options.
Combination of calcium channel blockers is a novel approach that has received scant attention in the literature or clinically. We uncommonly use any 2 agents from the same class of drugs simultaneously; however, the pharmacological heterogeneity of calcium channel blockers allows either verapamil or diltiazem to be combined with a dihydropyridine, producing additional lowering of the blood pressure, usually without significant increases in side effects. In the case described, dual calcium channel blocker therapy proved to be an economic and well-tolerated plan, although other options
. . . [Full Text PDF of this Article]
Author Affiliations
University of Florida Gainesville
|