
Reducing Antihypertensive Medication Use in Nursing Home Patients
Jack Froom, MD;
Jeffrey Trilling, MD
Arch Fam Med. 2000;9:378-383.
Of the 1.5 million nursing home residents, about 40% are aged 85 years or older, and a similar percentage have hypertension. The rates of incorrect diagnoses from the "white coat" effect and from errors in blood pressure evaluation are as frequent in older persons as in younger persons. The benefits of antihypertensive treatment and the risks of lowering blood pressures in the very old (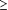 85 years) are uncertain. Elderly patients experience adverse effects from drug treatment that are unique to their age group and that complicate management problems associated with polypharmacy and multiple comorbid conditions. Trials to withdraw or lower the dosage of antihypertensive medications have been successful in up to 40% of elderly persons when combined with salt restriction and weight loss, but such studies are lacking in nursing home patients. The management of hypertension should be reevaluated in nursing home patients. 85 years) are uncertain. Elderly patients experience adverse effects from drug treatment that are unique to their age group and that complicate management problems associated with polypharmacy and multiple comorbid conditions. Trials to withdraw or lower the dosage of antihypertensive medications have been successful in up to 40% of elderly persons when combined with salt restriction and weight loss, but such studies are lacking in nursing home patients. The management of hypertension should be reevaluated in nursing home patients.
From the Department of Family Medicine, State University of New York at Stony Brook.
RELATED ARTICLE
The Archives of Family Medicine Continuing Medical Education Program
Arch Fam Med. 2000;9(4):375-377.
FULL TEXT
|