
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Pharmacology of Capacitative Calcium Entry
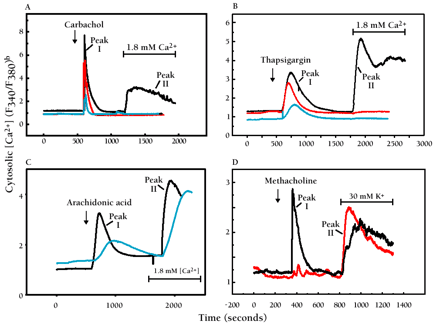
Selective blockade of capacitative calcium entry by 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2APB).a
A. The response of HEK293 cells (in Ca2+-free medium) to the cholinergic agonist carbachol (100 μM) is shown (black trace) as in Figure 1A. Capacitative calcium entry upon addition of Ca2+ (Peak II) is completely blocked by 30 μM 2APB (red trace). A higher concentration of 2APB (100 μM, blue trace) is required to inhibit the IP3-dependent transient response (Peak I) to carbachol.
B. The response of HEK293 cells (in Ca2+-free medium) to thapsigargin (1 μM) is shown (black trace) as in Figure 1B. 2APB (30 μM, red trace; 100 μΜ, blue trace) also inhibits this response.
C. The activation of channels in HEK293 cells upon treatment with arachidonic acid (30 μM; black trace) is not inhibited by 2APB at 100 μM (blue trace).
D. In AR4-2J cells, a pancreatoma cell line, a phospholipase C–dependent response to cholinergic agonist methacholine (100 μM) as well as L-type Ca2+ channel activation in response to elevated K+ are evident in the absence of 2APB (black trace). As shown by the red trace, 2APB (75 μM) completely blocks the IP3-dependent response, but does not block the activation of L-type voltage dependent Ca2+ channels by elevated external K+.
aData for panels A, B, and C come from (24).
bF340/F380 is the fluorescence shift of the Ca2+ indicator Fura-2.


