
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
A GABAB Mystery: The Search for Pharmacologically Distinct GABAB Receptors
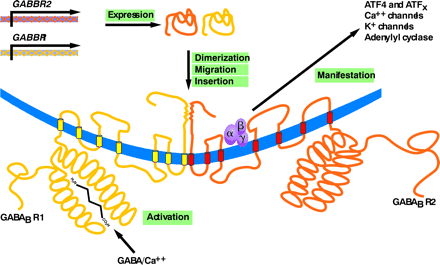
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of GABAB receptor (GABABR) assembly and function. The biogenesis of functional GABABRs depends on distinct genes (GABBR1 and GABBR2), the expression of which results in distinct seven-transmembrane–domain products that undergo heterodimerization, followed by migration (trafficking) and insertion into the plasma membrane. Activation of the R1 protomer by GABA and Ca2+ is manifested through a number of transduction mechanisms that are mediated through association of the R2 protomer with a trimeric (α, β, γ) G protein.


