
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Inhibition of Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-B):
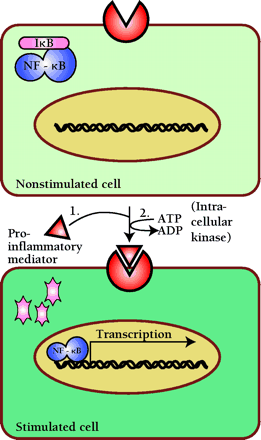
Figure 1.
In the absence of inflammatory activity, the transcription factor NF-κB is retained in the cytoplasm by a protein inhibitor (IkB). Proinflammatory stimuli activate a specific protein kinase, resulting in the degradation of IκB (pink) and translocation of NF-κB into the nucleus. (Details are elaborated in Figure 3.)


