
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Addiction: Making the Connection Between Behavioral Changes and Neuronal Plasticity in Specific Pathways
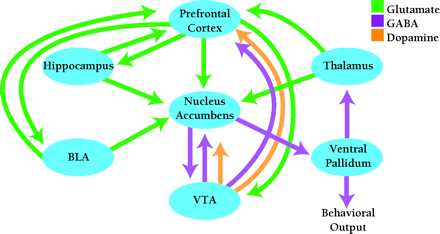
The neural circuitry involved in drug addiction. The nucleus accumbens, an interface between limbic and motor systems, plays a central role in this circuitry. Goal-directed behaviors are elicited by glutamate projections from limbic and cortical regions to the nucleus accumbens, while projections from the nucleus accumbens to motor regions are responsible for motor execution of these behaviors. Dopamine neurons located in the VTA innervate many limbic and cortical regions important for addiction, including nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex. Dopamine and glutamate inputs typically converge on common postsynaptic targets. BLA, basolateral amygdala; VTA, ventral tegmental area. [Based on (7).]


