
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Addiction: Making the Connection Between Behavioral Changes and Neuronal Plasticity in Specific Pathways
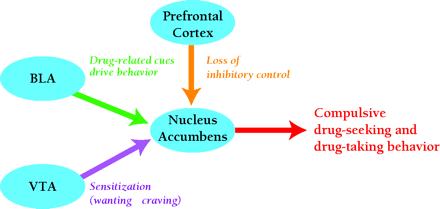
Possible relationships between neuronal plasticity in particular pathways and behavioral changes that lead to addiction. Several types of behavioral changes may contribute to compulsive drug-seeking and drug-taking behavior in addicts. Alterations in transmission between the BLA and the nucleus accumbens may strengthen stimulus-reward learning, increasing the ability of drug-related cues to control behavior. Sensitization of the incentive-motivational effects of drugs, due to alterations in transmission between the VTA and the nucleus accumbens, may transform drug “wanting” to “craving”. Alterations in transmission between the prefrontal cortex and limbic targets, including nucleus accumbens, may lead to impairment of inhibitory control mechanisms that normally govern reward-seeking behavior. Ultimately, drug-seeking behavior depends on glutamate transmission in the nucleus accumbens. BLA, basolateral amygdala; VTA, ventral tegmental area. [Based on (37).]


