
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Addiction: Making the Connection Between Behavioral Changes and Neuronal Plasticity in Specific Pathways
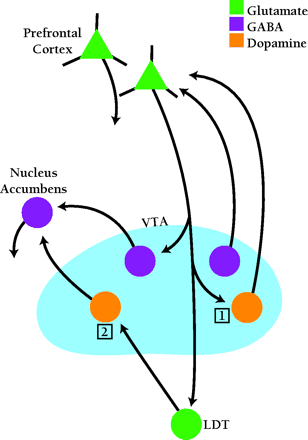
Possible sites for LTP in the ventral tegmental area during the induction of behavioral sensitization. The VTA contains dopamine neurons that project to nucleus accumbens (mesoaccumbens dopamine neurons) and dopamine neurons that project to prefrontal cortex (mesoprefrontal dopamine neurons). Likewise, the VTA contains mesoaccumbens GABA neurons and mesoprefrontal GABA neurons. VTA dopamine and GABA neurons also innervate other brain regions not shown in the diagram. Glutamate projections from the prefrontal cortex synapse on mesoaccumbens GABA neurons but not mesoaccumbens DA neurons, and on mesoprefrontal DA neurons but not mesoprefrontal GABA neurons (68). Some evidence suggests that prefrontal cortex also communicates with mesoaccumbens dopamine neurons indirectly, via projections to the LDT. The LDT sends both glutamate and cholinergic projections to mesoaccumbens dopamine neurons (71). The cholinergic fibers are not shown in the diagram. Based on this anatomy and other evidence, two possible sites are proposed for cocaine-induced LTP leading to the initiation of behavioral sensitization. Site 1: Excitatory synapses between prefrontal cortical projections and mesoprefrontal dopamine neurons. Site 2: Excitatory synapses between LDT projections and mesoaccumbens dopamine neurons. VTA, ventral tegmental area; LDT, laterodorsal tegmentum. [Based on (68).]


