
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Identification of TOR-interacting Proteins
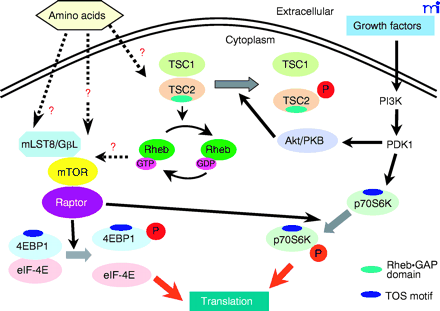
A working model for the mTOR signaling pathways in mammals. Nutrients regulate mTOR signaling pathway and Raptor and mLST8/GβL are components of the mTOR signaling complex. Raptor serves as a scaffolding protein that binds p70S6 kinase (p70S6K) and eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) through their TOR-signaling (TOS) motifs and Raptor facilitates their phosphorylation by mTOR. mLST8/GβL is another component of the mTOR signaling complex. mLST8/GβL interacts constitutively with the kinase domain of mTOR. The right side of the figure outlines a tentative pathway that links growth factor–dependent Akt/PKB activation through phosphatidylinositol-3’ kinase (PI3K) and phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1) to the stimulation of mTOR-dependent responses. The tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) proteins TSC1 and TSC2 serve as negative modulators of the mTOR pathway. The small GTPase Rheb (Ras homolog enriched in brain) is a direct target of TSC2’s intrinsic GTPase-activating function. Rheb•GTP appears to be a positive modulator of mTOR signaling. PKB, protein kinase B.


