
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Sodium-Dependent Neurotransmitter TRANSPORTERS: OLIGOMERIZATION as a Determinant of Transporter Function and Trafficking
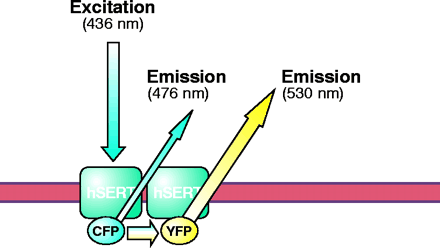
FRET methodology. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) is a quantum physical phenomenon that occurs only if two fluorophores are in sufficiently close proximity (<100 Å) and in an appropriate relative orientation. When these two criteria are met, an excited fluorophore (donor) can transfer its energy to a second, longer-wavelength fluorophore (acceptor) in a non-radiative manner. Among the spectral variants of the green fluorescent protein (GFP), the cyan and yellow fluorescent proteins (CFP and YFP) enjoy widespread use. The figure shows these fluorescent proteins fused to the N terminus of SERT. Enhancement of the acceptor (YFP) emission results from transfer of energy from the donor molecule (CFP); the donor emission diminishes concomitantly. In this case, the energy transfer is indicative of physical association of two (or more) SERT molecules in the plasma membrane.


