
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Neuronal Nicotinic Receptor Subtypes: DEFINING THERAPEUTIC TARGETS
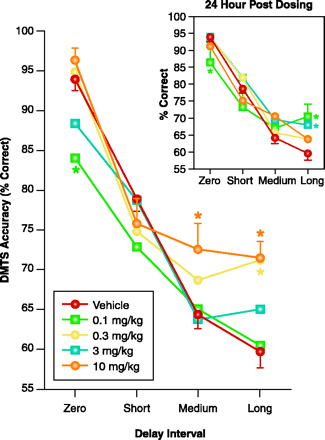
Cotinine-mediated task performance in Rhesus monkeys. Delayed matching-to-sample (DMTS) task performance was initiated ten minutes following the intramuscular administration of cotinine. The inset shows results of DMTS sessions run twenty-four hours after cotinine administration. Asterisks indicate significant differences (P<0.05) from mean accuracy values obtained after administration of drug vehicle (sterile normal saline). The results derived from seven Rhesus monkeys support preliminary studies indicating that cotinine-enhanced task accuracy in a dose-dependent manner, particularly during Long-delay trials (most difficult). Unexpectedly, the lowest dose (0.1 mg/kg) significantly decreased accuracy during Zero-delay trials (near simultaneous matching). Usually, a decrease in the performance of the shortest-delay trials suggests a decrease in attention. The particular improvements obtained during Long-delay trials suggest that cotinine, like nicotine, can augment aspects of retrieval or recall. Also, like nicotine, the positive mnemonic effects of cotinine extended to the day after drug administration (see inset). Even the decrease in accuracy during Zero-delay trials produced by the 0.1 mg/kg dose was evident.


