
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Mast Cells: The Missing Source of Cardiac Renin?
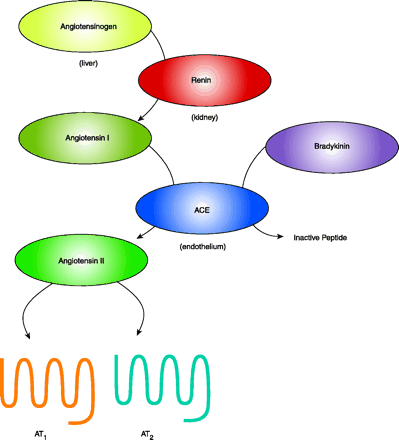
Figure 1.
The renin-angiotensin pathway (RAS). This figure emphasizes only part of the complexity of the RAS. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) both creates a vasoconstrictor (angiotensin II) and eliminates a vasodilator (bradykinin). Cathepsin D has weak in vitro renin-like activity that may be insignificant under physiologic conditions. Chymase has ACE-like activity, but the in vivo role of chymase is still under debate. AT1 (Angiotensin II Type 1) and AT2 are the seven-transmembrane-spanning receptors for the biologically active peptide angiotensin II (1).


