
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Recombinant Pharmaceuticals from Plants: The Plant Endomembrane System as Bioreactor
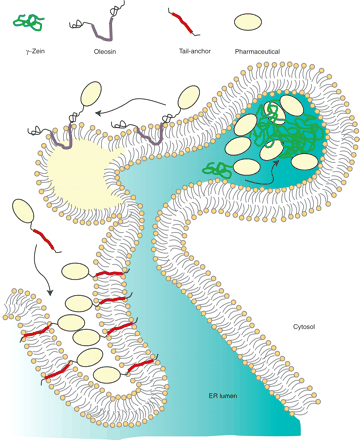
Strategies to accumulate high amounts of recombinant pharmaceuticals in the ER and ER-derived oil bodies. Through the use of plant protein domains (e.g., zein domains, oleosins, or tail-anchors), multiple protein fusions have been examined. Zein domains allow protein body formation within the ER lumen. Oleosin fusion products are first inserted into the external monolayer of the ER bilayer and then integrated into a nascent oil body (yellow). The tail anchor “anchors” recombinant proteins to the ER surface; upon overexpression, the ER can be commandeered in this way to develop distinct topologies that increase the stability of recombinant proteins. The hydrophobic domains of oleosin and of tail-anchored proteins are indicated in violet and red, respectively. Note that the N-terminal and C-terminal domains of oleosin are in the cytosol, and the very short C-terminal sequence of the tail-anchor is instead luminal.


