
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonists: Preclinical Promise for Treating Obesity and Cognitive Disorders
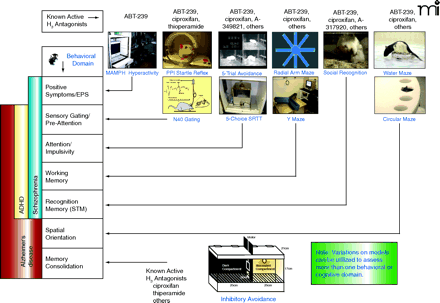
H3receptor antagonists exhibit broad efficacy in preclinical models of cognition. Animal models depicted across the top are used to analyze the cognitive behavioral domains (indicated by connecting arrows to respective domains in left column) thought to be important for human diseases such as ADHD, Alzheimer’s Disease, or schizophrenia (53). The animal models where H3 antagonists have been shown to be efficacious include (from the left): 1) reduction of methamphetamine (MAMPH) hyperactivity; 2) enhancement of prepulse (PPI) inhibition of startle and N40 gating responses; 3) 5-trial inhibitory avoidance and 5-choice serial reaction time test (SRTT); 4) radial arm maze and Y maze; 5) social recognition; 6) water maze and circular maze; and 7) inhibitory avoidance. The indicated efficacious H3 receptor antagonists, such as ciproxifan and ABT-239, that are shown above each animal behavioral model are not intended to constitute a comprehensive list of all H3 antagonists tested in these models but to illustrate the broad efficacy of H3 receptor antagonists across cognitive domains.


