
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
CALCIUM: A Role for Neuroprotection and Sustained Adaptation
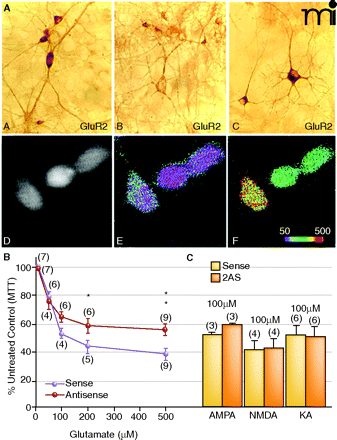
Dissociation between elevated Ca2+permeability and neurotoxicity. A. GluR1A and GluR2B immunolabeling of hippocampal neurons sevety-two hours after exposure to GluR2B AS-ODNs. (A). In sense strand–treated controls, GluR2B protein expression was intense and uniform within the somata and weaker in the dendrites of single cells. (B). After GluR2B knockdown, somatic immunolabel was highly reduced at this time. (C). In sister cultures, GluR1A protein detection was intense within the cell body as well as proximal and distal dendritic processes indicating a rise in the GluR1:2 ratio. Ca2+ imaging experiments showed corresponding pharmacological rises in AMPA receptor-mediated Ca2+ permeability. (D). Basal Ca2+ levels in GluR2B AS-ODN–treated culture. (E). Pseudocolor micrographs of basal Ca2+ levels in GluR2B AS-ODN–treated culture. (F). Puff application of AMPA under the same conditions significantly increased [Ca2+]i in the same neurons. B. and C. Effect of GluR2B knockdown on L-glutamate- (B) or KA- (C) treatment on cell viability in hippocampal cultures. On day twelve, cultures were treated with GluR2B AS-ODNs, and on days thirteen or fourteen, cultures were treated with excitotoxins. Data represent the mean ± SEM of 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) mean values at 570 nm that were quantified from control and experimental hippo-campal cultures. Modified from (77, 143). Reprinted with permission.


