
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
On Cotransmission & Neurotransmitter Phenotype Plasticity
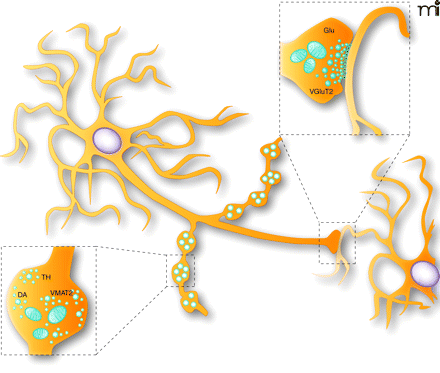
Schematic representation of the synaptic and non-synaptic axon terminals established by dopamine neurons. DA neurons are known to establish two morphologically distinguishable axon terminals: some that are non-synaptic and others that are synaptic. The non-synaptic terminals (varicose-like structures) display no obvious pre- and postsynaptic specialization (see lower illustration showing a magnified view of a single non-synaptic terminal), contain tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and could be specialized for the release of DA. The synaptic terminals display a more classical active zone, postsynaptic density and synaptic cleft, and could be the site of VGluT2 expression and of glutamate (Glu) release (see upper illustration showing a magnified view of a synaptic axon terminal).


