
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Shell Shock: An Old Injury with New Weapons
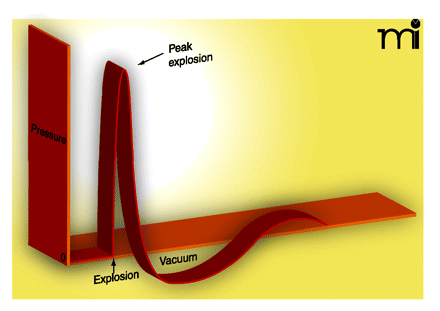
Figure 1.
Schematic of a Friedlander waveform showing changes in atmospheric pressure following a blast explosion. Prior to an explosion, air pressure is normal. Immediately after the explosion, air pressure rapidly rises to a peak overpressure. This is followed by a drop in atmospheric pressure to below normal, creating a relative vacuum. After the blast wave subsides, atmospheric pressure equilibrates and returns to normal.


