 |
May-August 2016
Volume 4 | Issue 2
Page Nos. 25-43
Online since Wednesday, September 14, 2016
Accessed 8,486 times.
PDF access policy
Journal allows immediate open access to content in HTML + PDF
EPub access policy
Full text in EPub is free except for the current issue. Access to the latest issue is reserved only for the paid subscribers.
|
| |
|
|
Show all abstracts Show selected abstracts Add to my list |
|
| ORIGINAL ARTICLES |
|
|
  |
Quality of life in subjects with shortened dental arch rehabilitated with removable metal-based partial dentures |
p. 25 |
Julie O Omo, Mathew A Sede, Temitope Ayodeji Esan
DOI:10.4103/2347-4610.190606 Context: Previous studies showed that treatment of shortened dental arch (SDA) subjects with metal-based removable partial denture (RPD) did not significantly improve their quality of life (QoL). Objective: To assess the effect of metal-based RPDs on the QoL of patients in Nigeria with SDA using the oral health impact profile 49 (OHIP-49). Materials and Methods: The study was an interventional study consisting of 36 consecutive patients attending the Prosthetic Dental Clinic of the University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Benin City, Nigeria and met the inclusion criteria. The patients completed the OHIP-49 questionnaire before treatment and 3 months after insertion of the metal-based denture. All the relevant information gathered from the subjects was recorded in the data collection sheet. Data analysis was done using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS 17.0). Statistical significance was inferred at P < 0.05. Results: A total of 36 patients consisting of 24 (66.7%) females and 12 (33.3%) males participated in the study. The age range of the subjects was 34-64 years with a mean age of 52.2 ± 8.2 years. There was a significant improvement in the mean scores of all the domains of OHIP-49 and the total mean score of OHIP-49 3 months after treatment. Irrespective of age, gender, saddle type, and saddle location, there was a significant improvement in the QoL of the patients 3 months after treatment with metal-based RPD. Conclusion: Within the limitations of this study, there was an improvement in the QoL of subjects with SDA after treatment with RPDs. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
  |
Evaluation of fit accuracy of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing crowns fabricated by three different digital impression techniques using cone-beam computerized tomography |
p. 32 |
Noha M Salem, Sanaa H Abdel Kader, Fayza Al Abbassy, Amir S Azer
DOI:10.4103/2347-4610.190609 Purpose: The aim of this in vitro study was to evaluate the fit accuracy of computer-aided design (CAD)/computer-aided manufacturing lithium disilicate full contour crowns fabricated by three different digital impression techniques. Materials and Methods: An acrylic upper first molar was prepared to receive a full ceramic crown and used to fabricate ten ceramic master dies using lost wax and heat press techniques. Each ceramic die was seated in a typodont model and ten polyvinyl siloxane impressions were made for the dies and neighboring teeth to fabricate ten stone casts. Three groups of lithium disilicate crowns (n = 10) were fabricated; Group E: Crowns were fabricated by scanning the ten stone casts with in Eos X5 extraoral scanner. Group O: Crowns were fabricated by powder-free scanning of the ten ceramic dies in their typodont models with CEREC Omnicam. Group B: Crowns were fabricated by CEREC Bluecam optical impressions of the ceramic dies in their typodont models after titanium dioxide powder application. All the specimens were milled from IPS e-max CAD blanks. Each crown was evaluated on its die for fit accuracy using computerized cone-beam tomography at seventy measuring points. The variability among the three groups was evaluated using one-way ANOVA test at P < 0.05. Results: No statistically significant difference was found among the three groups for overall results at (P = 0.658), whereas Group E showed significantly better marginal fit with a mean value of 76 ± 39.0 μm at P = 0.047. Conclusions: All tested digital impression techniques showed clinically acceptable accuracy and extraoral scanning significantly enhanced the marginal fit. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| CASE REPORT |
 |
|
|
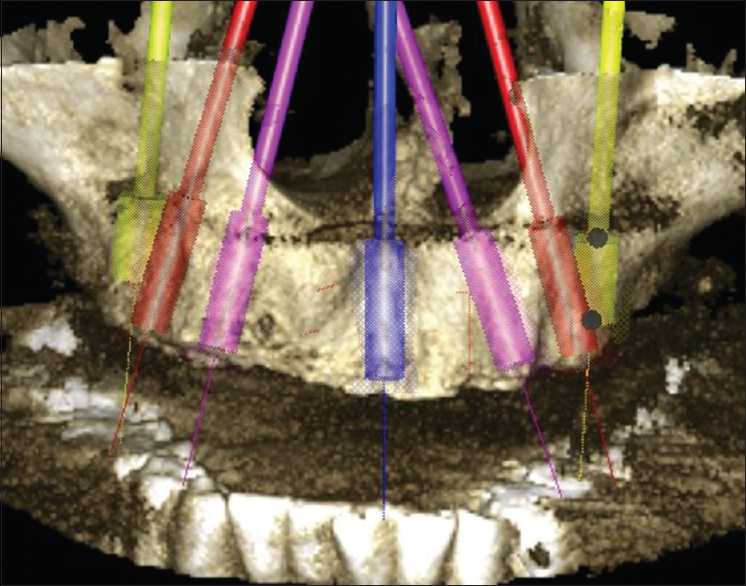  |
Rehabilitation of edentulous maxillary arch with implant-assisted fixed complete prosthesis using multi-unit straight and angulated abutments |
p. 37 |
Marut Pradipbhai Patel, S Anilkumar, Rajesh Chankramath, Sandhya Gopalakrishnan
DOI:10.4103/2347-4610.190610 In comparison to an edentate mandible, rehabilitation of a completely edentulous maxilla using osseointegrated implants has always tested the ability of clinician and laboratory technician. Complex anatomy, as well as the biomechanical limitations of the maxillary bone, resists the placement of implant in its ideal location. This article illustrates a two-stage surgical and prosthetic management of edentulous maxilla opposing natural teeth using seven implants. This case report highlights the advantages of multi-unit straight and angulated abutments, torqued onto the implants, over which a cast titanium framework was made for fabrication of implant-assisted fixed complete dental prosthesis (FP-3 prostheses). |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| LETTERS TO EDITOR |
 |
|
|
|
Polyetheretherketone implants: Can they replace titanium in future |
p. 41 |
Sunil Kumar Mishra, Ramesh Chowdhary, Puja Hazari
DOI:10.4103/2347-4610.190612 |
| [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Do antidepressant drugs leads to dental implant failure |
p. 42 |
Sunil Kumar Mishra, Puja Hazari, Ramesh Chowdhary
DOI:10.4103/2347-4610.190614 |
| [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|