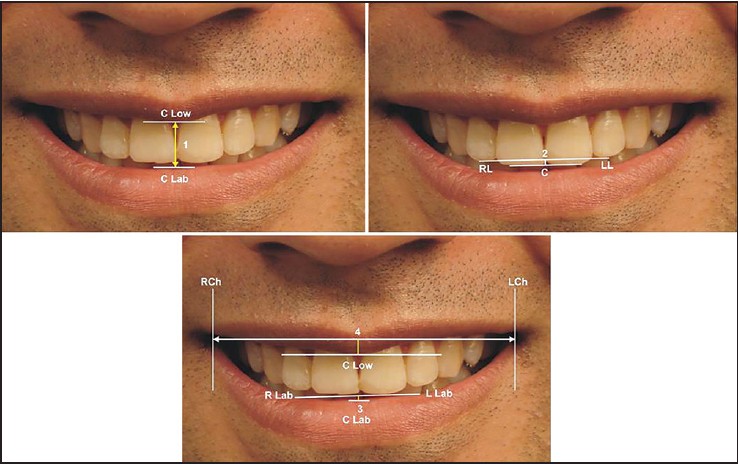
Figure 4: Linear measurements in the vertical plane: 1. Smile height- Distance from the most inferior point on the upper lip between the maxillary central incisors to the most superior point on the lower lip, on a perpendicular vertical line from the upper point (C Low to C Lab). 2. Length of the perpendicular ofthe arc of the upper incisor- Perpendicular distance from the straight edge through points RL and LL to point C. 3. Length of the perpendicular for the arc of the lower lip-Perpendicular distance from the straight edge through points RLab and LLab to point C Lab. 4. Upper lip curvature (Positive or Negative)-A straight edge was aligned through points RCh and LCh, and point C Low was observed to determine whether or not the point was inferior or superior to the line established determined as positive if the corners of the smile were superior to the center of the upper lip, andnegative if the corners of smiles were below the corner of upper lip