
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Epigenetic Downregulation of GABAergic Function in Schizophrenia: Potential for Pharmacological Intervention?
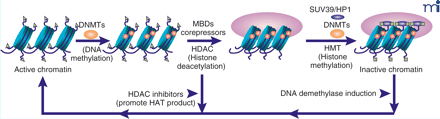
Chromatin remodeling processes. The cartoon depicts changes that occur as chromatin is remodled from active chromatin inactive chromatin. The transition is a multi-step process that involves: a) DNA methylation by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs); b) binding of methyl CpG dinucleotides by MBD proteins; c) histone deacetylation by HDACs; d) HMTs (e.g., SUV39) that methylate histones and that are recruited by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins (e.g., HP1). HDAC inhibitors can reactivate gene transcription by increasing histone tail acetylation, which relaxes chromatin. The DNA demethylase activity of MBD2 may be involved in reversing the methylation of promoter regions, a first step in reversing gene silencing. MBD, methyl binding domain proteins; HDAC, histone deacetylase; HMT, histone methyltransferase; HP1, heterochromatin binding protein; DNMT, DNA methyl transferase. Green triangles represent the acetylation of histone tails. Green boxes represent the methylation of histones. Figure is modified from (33).


