
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Fibrin Mechanisms and Functions in Nervous System Pathology
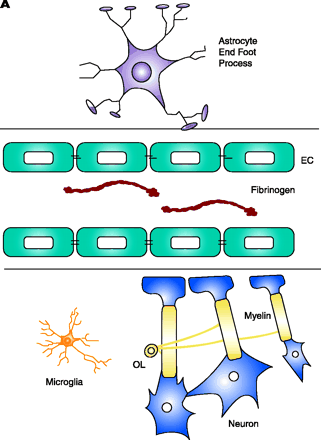
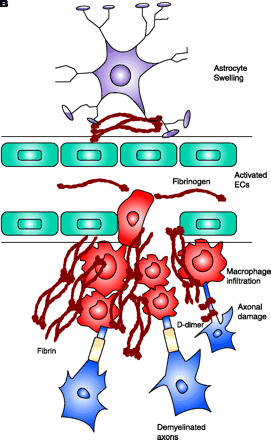
Schematic representation of fibrin extravasation in the neurovascular unit. A. Neurons and astrocytes are in close proximity with brain endothelial cells and their interactions form a functional unit, termed the neurovascular unit (11). Tight junctions between the endothelial cells (EC) confine fibrinogen in the vasculature. B. After vascular damage leading to disruption of the BBB, fibrinogen gains access within the CNS parenchyma with consequent fibrin formation. In MS, fibrin deposition correlates with the sharp border of demyelination (141), colocalizes with macrophage infiltration (80), with axonal damage (81, 92), and with astrocyte swelling and tight junction abnormalities (82). Fibrinogen molecule adapted from (33).


