
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
NEURONAL PDZ DOMAINS: A Promising New Molecular Target for Inhaled Anesthetics?
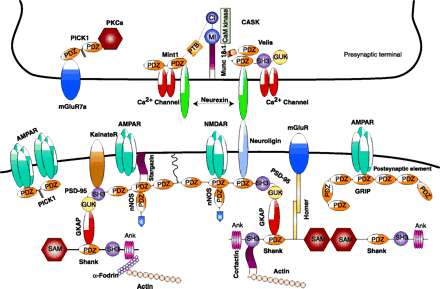
Neuronal PDZ domain–organized macromolecular signaling complexes at the synapse. The intercellular junction is formed by neurexin and neuroligin. On the presynaptic side, CASK interacts with neurexin through its PDZ domain. CASK also interacts with two PDZ domain–containing proteins, Velis and Mint1, and with N-type Ca2+ channels. The PDZ domains of Mint1 bind to N-type Ca2+ channels, and its N-terminus interacts with Munc 18-1 and CASK. In addition, the PDZ domain of PICK1 (protein interacting with C kinase-1) interacts with the C terminus of metabotropic glutamate receptor subunit 7a (mGluR7a) and the catalytic subunit of protein kinase Cα (PKCα). On the postsynaptic side, the PDZ domains of PSD-95 interact with the PDZ domain of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) and with the C-termini of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR), neuroligin, and the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate (AMPA) receptor (AMPAR)- targeting protein stargazin. The Src homology 3 (SH3) domain of PSD-95 binds to kainate receptors (KainateR). PSD-95 is attached to the postsynaptic membrane via the N-terminal palmitate group (wiggly line). The guanylate kinase (GUK) domain of PSD-95 interacts with guanylate kinase domain-associated protein (GKAP), and the C-terminal tail of GKAP directly binds to the PDZ domain of Shank. Shank also couples the metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) via the bridge protein Homer. Shank can multimerize via its sterile alpha motif (SAM) domain and is directly linked to the cytoskeleton via two actin-binding proteins: cortactin and α-fodrin. The AMPA receptors also bind to two additional PDZ proteins GRIP/ABP (glutamate receptor-interacting protein/AMPA receptor–binding protein) and PICK1 via PDZ domain-mediated protein interactions. MI, Munc 18-1-interaction domain; CI, CASK interaction domain; Ank, ankyrin repeat.


