
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
NEURONAL PDZ DOMAINS: A Promising New Molecular Target for Inhaled Anesthetics?
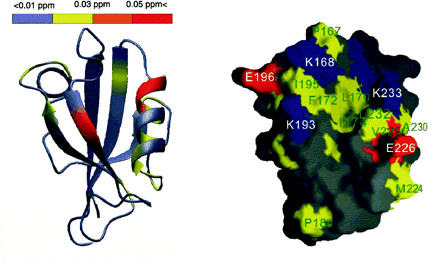
Chemical-shift changes of PSD-95 PDZ2 resulting from halothane binding. A. The horizontal bar at the top of the figure represents the coloring scheme. The figure was prepared using the program MOLMOL. The red color represents the largest changes, followed by orange, and then yellow. The gray means no change after adding halothane. The peptide-binding groove of PSD-95 PDZ2 had the most extensive and largest changes, indicating it is also the halothane binding site. B. Surface representation of the target-binding pocket of PSD-95 PDZ2. The hydrophobic residues are shown in yellow, negatively charged residues in red, positively charged residues in blue, and the polar amino acids in gray. The orientation of the PDZ domain is identical to that shown on left. Reprinted by permission of the
Journal of Biological Chemistry278, 36669–36675ASBMB © 2003.


