
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonists: Preclinical Promise for Treating Obesity and Cognitive Disorders
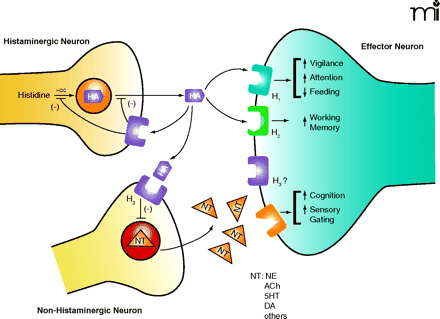
Schematic representation of H3receptor function. Stimulation of presynaptic H3 autoreceptors on histaminergic neurons by histamine (HA) inhibits the synthesis of histamine [through histidine decarboxylase (HDC)] and also inhibits the release of HA from the neuron. Similarly, stimulation of presynaptic H3 heteroreceptors on non-histaminergic neurons inhibits the release of a number of neurotransmitters (NT), including norepinephrine (NE), acetylcholine (ACh), serotonin (5HT), dopamine (DA), and others. These neurotransmitters can then activate their respective target receptors postsynaptically to evoke a variety of physiological responses as indicated in the figure.


