
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Unraveling the Story of NGF-mediated Sensitization of Nociceptive Sensory Neurons: ON or OFF the Trks?
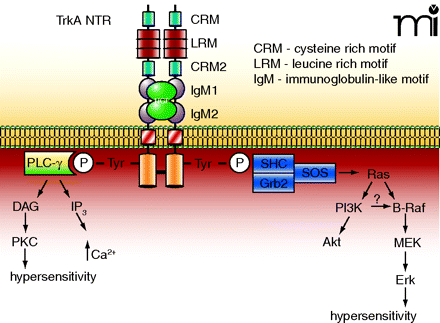
The TrkA NTR and its associated intracellular signaling pathways. The TrkA NTR is made up of multiple extracellular domains that consist of two cysteine-rich motifs (CRM), three leucine rich motifs (LRM) and two immunoglobulin-like motifs (IgM). Binding of NGF results in dimerization and the cross-phosphorylation of tyrosine residues on the intracellular signalling domains. These tyrosines form the binding sites for the scaffolding proteins Shc-Grb2-SOS, which leads to the activation of the small G-protein Ras, followed by activation of the serine-threonine kinases Raf, MEK, and the MAPK, Erk. In sensory neurons, the activation of Erk has been linked to hypersensitivity. Ras can also activate PI3K and its downstream effector Akt. In some cells, PI3K can activate B-Raf which leads to phosphorylation of Erk. The phosphorylated tyrosines also form the binding site for PLC-γ, which consequently results in the activation of PKC. It is well established that PKC plays an important role in regulating the sensitivity of sensory neurons to noxious stimulation.


