
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Regulation of Receptors and Transporters by Ubiquitination: New Insights into Surprisingly Similar Mechanisms
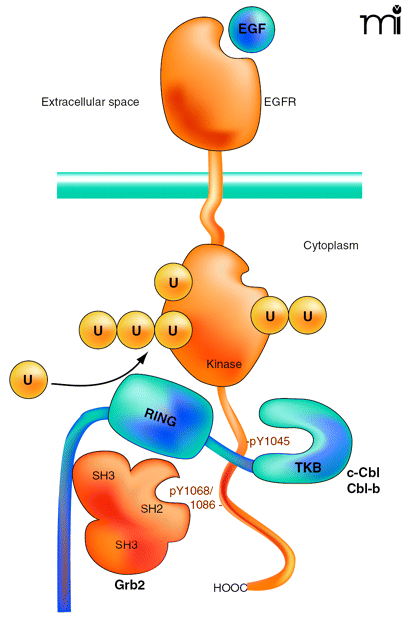
Interactions of the EGF receptor leading to receptor ubiquitination. EGF binding activates the receptor tyrosine kinase and results in phosphorylation of Tyr1045, Tyr1068, and Tyr1086 in the C terminus of the receptor. The SH3 domains of Grb2 are associated with the C terminus of c-Cbl or Cbl-b. A Grb2-Cbl complex binds to the receptor by means of the interaction of the SH2 domain of Grb2 with phosphorylated Tyr1068 or phosphorylated Tyr1086 (pY1068/86) and the tyrosine kinase binding (TKB) domain of c-Cbl or Cbl-b interacts with the phosphotyrosine 1045 (pY1045) of the receptor. Recruitment of E2 (not shown) to the RING domain of Cbl results in covalent attachment of monoubiquitin and polyubiquitin chains to the kinase domain of the receptor.


