
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Lighting a Backfire to Quench the Blaze: A Combined Drug Approach Targeting the Vanilloid Receptor TRPV1
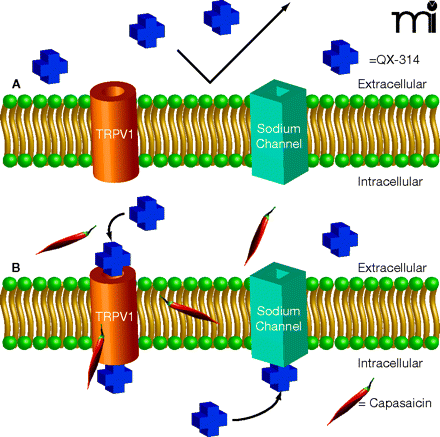
Combined treatment with capsaicin and positively charged sodium channel blocker to selectively inhibit C-fiber sensory neurons. A) The voltage-dependent sodium channel blocker QX-314 is unable to pass through the membrane on account of its positive charge. B) The vanilloid agonist capsaicin opens the TRPV1 channel, permitting the positively charged QX-314 to enter the cell through the relatively large pore of this channel. Upon gaining access to the interior of the cell, QX-314 inhibits the neuronal voltage-dependent sodium channel. Because TRPV1 channels are only present on the C-fiber sensory neurons, the action of the sodium channel blocker is thus limited to these neurons.


