
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Potassium Channel Subunits: The MiRP Family
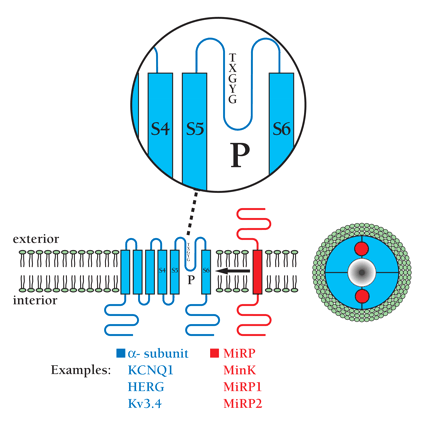
TheKCNE genes encode single-transmembrane–domain peptides (i.e., MiRPs) that regulate voltage-gated potassium (VGK) channels. VGK channels are formed by association of four α-subunits (blue). Each α-subunit contains six transmembrane domains and one pore-forming P loop (P; see inset). P loops contain the pentapeptide sequence TXGY/FG at the ion selectivity filter portion of the pore. In cells, potassium channel α-subunits interact with additional subunits, such as MiRPs (red), as well as membrane and cytosolic regulators (not shown). The MiRPs are encoded by KCNE genes and are a family of β-subunits that assemble (denoted by arrow) with α-subunits to generate native channels. The stoichiometry of MiRP subunits within each channel is not known; a possible α4β2 complex is shown (looking down onto the plane of the exterior membrane surface; right), suggesting close approximation of MiRP and the ion conduction pore (17, 73).


