
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Transcriptional Mechanisms Underlying Addiction-Related Structural Plasticity
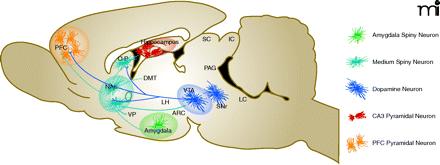
Structural plasticity of major cell types in the neural circuitry underlying addiction. Ventral tegmental area (VTA) dopamine projection neurons (solid purple lines) impinge directly upon nucleus accumbens (NAc) and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) neurons, as well as on amygdala and hippocampal neurons (the latter projections are not shown in the figure). GABAergic afferents (some direct, some indirect) from the NAc to the VTA (solid blue lines) provide feedback to VTA dopamine neurons. Glutamatergic afferents to the NAc from mPFC, amygdala, and hippocampus (dotted blue lines) release glutamate directly onto medium spiny neuron spine synapses. Each structure contains specialized neuronal cell types that play a critical role in the regulation of addiction-like behavior. The major cell types, color-coded in the key, include amygdala (green) and NAc (blue) spiny neurons, PFC (orange) and hippocampal CA3 (red) pyramidal neurons, and VTA dopamine neurons (purple). Drugs of abuse can alter the structure of each of these cell types as defined in the table above. oPFC, orbital prefrontal cortex. Modified from (5, 85) with permission.


