
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Transcriptional Mechanisms Underlying Addiction-Related Structural Plasticity
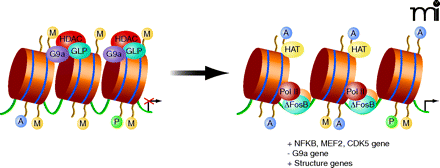
Cocaine induces chromatin modifications on gene promoters. As stated in Figure 2, methylation of histone 3 Lysine 9 (H3K9me2) causes chromatin condensation and gene repression. Under normal conditions, a complex of histone methyltransferases (HMTs) G9a, GLP, and histone deacetylases (HDACs) binds to histones and represses transcription. Following chronic cocaine administration, there is reduced binding of KMTs and HDACS, which, in combination with increased binding of histone acetyltransferases (HATs), ΔFosB, and RNA polymerase lI (POL II), results in a permissive state of chromatin and increased structural plasticity-related gene expression in NAc medium spiny neurons.


