Strontium Ranelate in Osteoporosis and Beyond: Identifying Molecular Targets in Bone Cell Biology
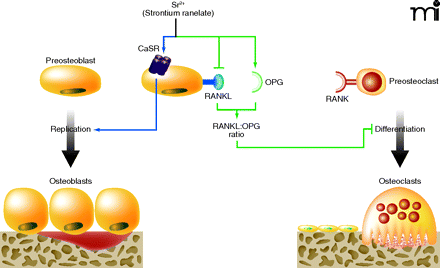
Figure 1
Mechanisms of action of strontium ranelate on bone cells. Activation (blue arrows) of the calcium sensing receptor (CaSR) by strontium ranelate in preosteoblasts (blue nucleus) increases osteoblast replication and number, which in turn results in increased bone formation. Strontium ranelate also acts on preosteoblasts (green arrows) to decrease the expression of RANKL (which binds RANK in preosteoclasts) and increases the expression of the decoy receptor osteoprotegerin (OPG), a dual effect that in turn results in reduced osteoclast differentiation and decreased bone resorption.



