Strontium Ranelate in Osteoporosis and Beyond: Identifying Molecular Targets in Bone Cell Biology
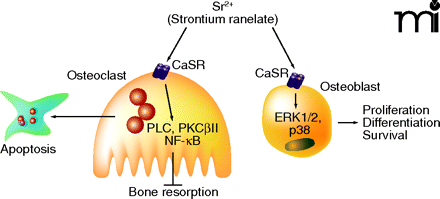
Figure 2
Signaling pathways induced upon activation of the calcium sensing receptor by strontium ranelate in bone cells. In osteoclasts, activation of the calcium sensing receptor (CaSR) by strontium ranelate induces activation of PLC, PKCβII, and NF-κB translocation, resulting in osteoclast apoptosis. In osteoblasts, strontium ranelate–induced activation of the CaSR induces activation of a number of kinases (e.g., ERK1/2 and p38MAPK, PLC, PKD, and PI3K), resulting in increased preosteoblast replication, osteoblast differentiation, and survival.



