
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Ceramide-1-phosphate: The “missing” link in eicosanoid biosynthesis and inflammation
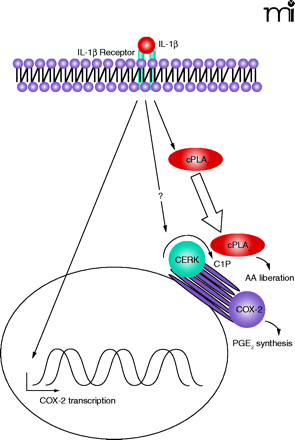
Role of CERK in eicosanoid synthesis. In response to inflammatory agonists, such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), the cell is “primed” for eicosanoid synthesis through induction of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). CERK then plays a pivotal role by producing C1P, a signaling molecule required for effective translocation (as indicated by the block arrow) of cPLA2α to the perinuclear membranes and consequential generation of AA. Conversion of AA to prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) represents the effective outcome of the inflammatory agonist. The question mark indicates that further signaling steps my prove to recruit CERK activity directly. Straight line arrows represent positive modulation of signal transduction; curved arrows indicate enzymatic reactions.


