
- Institution: Stanford Univ Med Ctr Lane Med Lib/Periodical Dept/Rm L109
- Sign In as Member / Individual
Collateral Damage in Cancer Chemotherapy: Oxidative Stress in Nontargeted Tissues
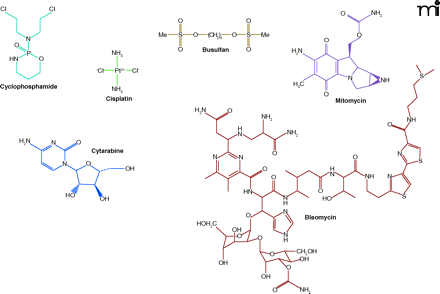
Anticancer drugs that cause oxidative stress. Cyclophosphamide and cisplatin are converted to reactive metabolites that cause DNA cross-linking and react with the thiol groups in enzymes and glutathione. Busulfan decreases glutathione levels. Mitomycin induces ROS generation through redox cycling of the quinone moiety. Cytarabine incorporates into DNA and acts as a chain terminator; following cytarabine-induced damage to DNA, ROS are generated in vivo. Bleomycin forms complexes with Fe2+ and O2 that break DNA strands and generate superoxide and hydroxyl radicals. In all, 56 of 132 FDA-approved anticancer drugs have been implicated in oxidative stress (as determined through Scinfinder Scholar using each drug name and the term “oxidative stress” as keywords). See text for details.


