 |
May-August 2015
Volume 3 | Issue 2
Page Nos. 27-56
Online since Friday, May 29, 2015
Accessed 15,828 times.
PDF access policy
Journal allows immediate open access to content in HTML + PDF
EPub access policy
Full text in EPub is free except for the current issue. Access to the latest issue is reserved only for the paid subscribers.
|
| |
|
|
Show all abstracts Show selected abstracts Add to my list |
|
| ORIGINAL ARTICLES |
|
|
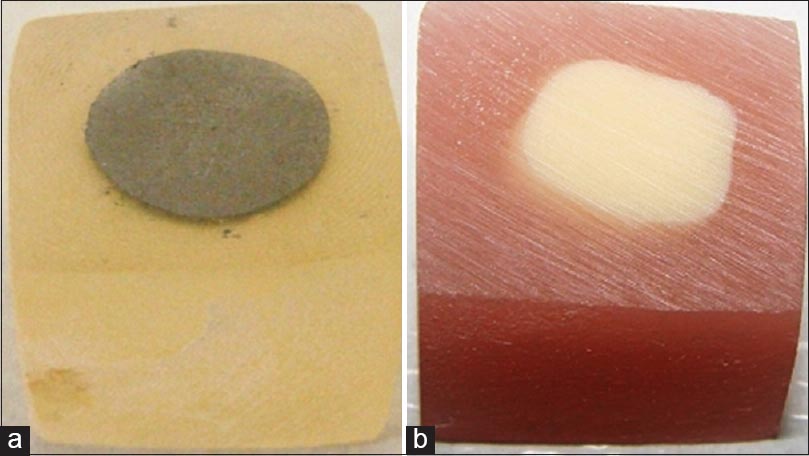  |
Effect of glass-fiber usage on bond strength of acrylic resin to components of removable partial denture |
p. 27 |
Tuğçe Baloglu, Bülent Kesim, Halil İbrahim Kılınç
DOI:10.4103/2347-4610.157813 Aim: In order to improve the mechanical properties of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), more attention has been directed toward the glass fibers due to its good reinforcement capability. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of glass fibers on the bond strength between reinforced acrylic resin and components of removable partial denture (RPD). Materials and Methods: Two types of denture teeth (conventional resin and cross-linked resin), two types of framework alloys (CoCr and Ti6Al4V) and heat-polymerized acrylic resin that was not reinforced and reinforced with glass fiber content of 1% and 5% were used. Reinforced and unreinforced acrylic resins were applied to both denture tooth and framework alloy samples to construct bonding area as 5 mm diameter. After polymerization of acrylic resin, samples were stored in distilled water for 2 days at 37°C; then they were thermocycled 5000 times (5-55°C). To record shear bond strength of samples, universal testing machine was used until failure occurred. The shear bond strength data were analyzed at 5% significance level. Results: The shear bond strength of CoCr alloy and cross-linked resin denture tooth samples didn't show any effect with reinforcement. But conventional resin denture teeth bonding enhanced with 5% fiber concentration; and Ti6Al4V, the addition of glass fiber, regardless of the ratio, affected the bonding strength in a positive way. Conclusions: Glass fiber reinforcement of the PMMA increased or did not aAQ4ffect, but never decreased the bonding strength between acrylic resin and component of RPD. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
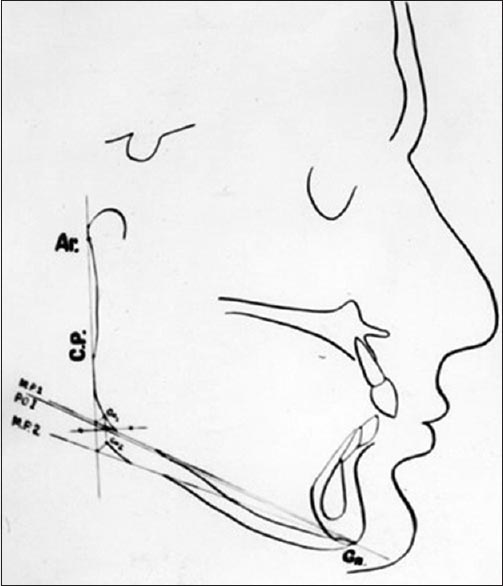  |
Validity of cephalometric approach to determine freeway space in edentulous cases |
p. 32 |
Ansuia Gupta, Ramandeep Singh Gambhir
DOI:10.4103/2347-4610.157820 Aims and Objectives: The aim was to determine freeway space in edentulous individuals by correlating clinical findings of freeway space clinically with the gonial angle cephalometrically. Materials and Methods: The study was conducted on 100 dentulous individuals in the age-group of 20-30 years. Freeway space was determined by the difference between the readings of vertical dimension of rest and vertical dimension of occlusion in dentulous individuals. Gonial angle was calculated with the help of cephalometric radiographs, and the two were co-related.Results: Gonial angle (X) varied from 103° to 104° with an average of 122.45°. Freeway space (Y) ranged from 0.9 mm to 2.9 mm with an average of 1.77 mm. Co-relation of 51.21% existed between the gonial angle and freeway space. Conclusion: The study establishes a co-relation between gonial angle and freeway space with a value of 51.215%. In this way, the value of freeway space can be obtained. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
  |
Marginal accuracy of metal copings produced with different ring casting techniques: An in vitro study |
p. 36 |
Vishal Singh, Sharad Gupta, Akshay Bhargava, Sridevi Kaul
DOI:10.4103/2347-4610.157824 Objective: Evaluation and comparison of marginal accuracy of three porcelain fused with metal alloy using ringless and closed ring casting techniques. Materials and Methods: A total of 60 metal copings was fabricated on a metal die. Specimens were divided into two groups (Group I ringless and II ring casting techniques) of 30 patterns each. Groups are further divided into three subgroups of 10 each representing porcelain fused to metal alloys castings namely Mealloy, Wiron-99, and Bellabond plus. The measurement of fit of the metal copings was recorded by stereo photomicroscope at four different surfaces. Results: No significant difference (P < 0.001) was found when the mean vertical marginal integrity at all the buccal, palatal, mesial and distal surfaces among three porcelain fused to metal alloys for both the groups. However on comparing in between group I and group II, it showed that there is significant difference (P > 0.001). The mean of the vertical integrity for the group I (Ringless) was less than group II (Closed Ring). Conclusions: Within the limitations of the study design, it can be concluded that there is a significant difference between ringless and closed ring casting but both are clinically acceptable. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| CASE REPORTS |
 |
|
|
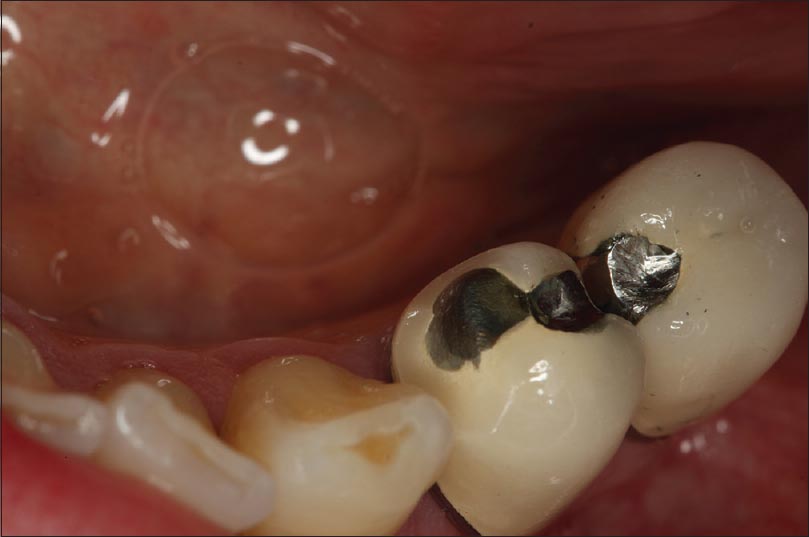  |
Repair of porcelain restorations: Four case reports |
p. 42 |
Hasan Hüseyin Kocaagaoglu
DOI:10.4103/2347-4610.157834 Porcelain has been used with prosthetic restorations for many years. Although their long term success has been demonstrated, failures may occur in metal-porcelain restorations due to trauma, laboratory failures or premature contacts. Damaged porcelain restorations can cause serious clinical and esthetic problems. In some situations, the production of a new restoration is difficult because of the high treatment costs. Porcelain repair may provide a practical alternative for patients and clinicians, especially those restorations with minor porcelain cracks. In the present series of case reports, repair of the fractured metal-porcelain restorations, using porcelain repair system and composite resin were demonstrated. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
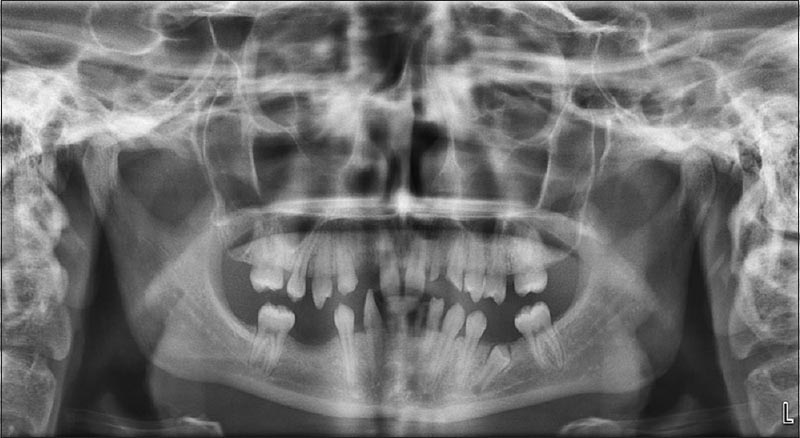  |
Prosthetic treatment of nonsyndromic oligodontia |
p. 47 |
Müjde Sevimay, Ceyda Akın
DOI:10.4103/2347-4610.157842 Oligodontia is the agenesis of six or more teeth, excluding the third molars. Genetic factors play an important role in oligodontia, which can occur as an isolated finding or as part of a syndrome. The characteristic dental symptoms are reduced number of teeth, reduction in tooth size, anomalies of tooth form, and delayed eruption. The absence of teeth in patients can cause aesthetic, functional, and psychological problems, particularly if the anterior region is involved. This case report describes the prosthetic treatment approach to a 19-year-old patient with nonsyndromic oligodontia characterized by the absence of 10 permanent teeth. The objectives of the treatment were the prosthetic restoration of the missing teeth and the provision of occlusion with full-mouth zirconia restorations. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
  |
Multidisciplinary approach in rehabilitating flabby ridge in completely edentulous patient |
p. 51 |
Poonam K Khinnavar, BH Dhanya Kumar, HR Shivakumar, DB Nandeeshwar
DOI:10.4103/2347-4610.157844 Hypermobile ridges or flabby edentulous ridges are a common occurrence. The mucostatic or minimally displacive impression technique is one of the treatment options in this scenario. Conventional mucostatic methods like employing a window tray technique, double spacers, multiple relief holes, can be utilized. Even the manual placement and manipulation of a custom tray may distort the tissues. This may violate the principles of mucostatic impression technique. Flabby ridges can be managed surgically by excision, ridge augmentation, injection of sclerosing solutions and also by implant retained prosthesis. Proper recording of these hypermobile tissues and stable occlusal contacts can help to manage flabby tissues to certain extent. This case report is about surgical and prosthodontic approach for management of a maxillary flabby edentulous ridge with the aid of a minimally displacive impression technique. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| LETTER TO EDITOR |
 |
|
|
|
The need for evidence-based practice in fixed and removable prosthodontics |
p. 56 |
Haroon Rashid
DOI:10.4103/2347-4610.157846 |
| [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|