|
Show all abstracts Show selected abstracts Add to my list |
|
| EDITORIALS |
|
|
|
Chromosomal aberrations in hematological malignancies: A guide to the identification of novel oncogenes |
p. 43 |
Babu Rao Vundinti, Kanjaksha Ghosh
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86168 PMID:22090710 |
| [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Are mannose-binding lectin gene 2 (MBL2) polymorphisms and MBL deficiency associated with infections? |
p. 45 |
Vandana Pradhan, Ajit Gorakshakar
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86170 PMID:22090711 |
| [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| REVIEW ARTICLE |
 |
|
|
  |
Craniosynostosis genetics: The mystery unfolds  |
p. 48 |
Inusha Panigrahi
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86171 PMID:22090712Craniosynsostosis syndromes exhibit considerable phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity. Sagittal synostosis is common form of isolated craniosynostosis. The sutures involved, the shape of the skull and associated malformations give a clue to the specific diagnosis. Crouzon syndrome is one of the most common of the craniosynostosis syndromes. Apert syndrome accounts for 4.5% of all craniosynostoses and is one of the most serious of these syndromes. Most syndromic craniosynostosis require multidisciplinary management. The following review provides a brief appraisal of the various genes involved in craniosynostosis syndromes, and an approach to diagnosis and genetic counseling.
|
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (3) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ORIGINAL ARTICLES |
 |
|
|
  |
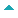
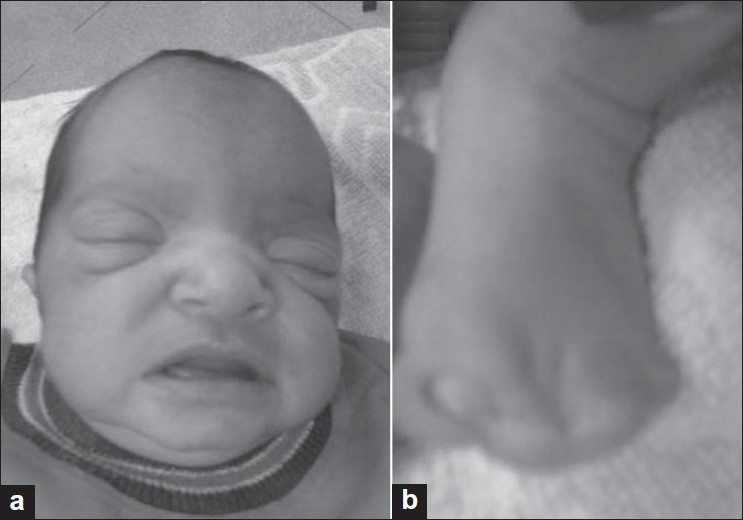
Characterization of cryptic rearrangements, deletion, complex variants of PML, RARA in acute promyelocytic leukemia |
p. 54 |
Pratibha Kadam Amare, Chanda Baisane, Reena Nair, Hari Menon, Shripad Banavali, Sharayu Kabre, Sumit Gujral, P Subramaniam
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86174 PMID:22090713Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is characterized by a reciprocal translocation t(15;17)(q22;q21) leading to the disruption of Promyelocytic leukemia (PML) and Retionic Acid Receptor Alpha (RARA) followed by reciprocal PML-RARA fusion in 90% of the cases. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) has overcome the hurdles of unavailability of abnormal and/or lack of metaphase cells, and detection of cryptic, submicroscopic rearrangements. In the present study, besides diagnostic approach we sought to analyze these cases for identification and characterization of cryptic rearrangements, deletion variants and unknown RARA translocation variants by application of D-FISH and RARA break-apart probe strategy on interphase and metaphase cells in a large series of 200 cases of APL. Forty cases (20%) had atypical PML-RARA and/or RARA variants. D-FISH with PML/RARA probe helped identification of RARA insertion to PML. By application of D-FISH on metaphase cells, we documented that translocation of 15 to 17 leads to 17q deletion which results in loss of reciprocal fusion and/or residual RARA on der(17). Among the complex variants of t(15;17), PML-RARA fusion followed by residual RARA insertion closed to PML-RARA on der(15) was unique and unusual. FISH with break-apart RARA probe on metaphase cells was found to be a very efficient strategy to detect unknown RARA variant translocations like t(11;17)(q23;q21), t(11;17)(q13;q21) and t(2;17)(p21;q21). These findings proved that D-FISH and break-apart probe strategy has potential to detect primary as well as secondary additional aberrations of PML, RARA and other additional loci. The long-term clinical follow-up is essential to evaluate the clinical importance of these findings. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (2) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The first report described as an important study: The association of mannose-binding lectin gene 2 polymorphisms in children with down syndrome |
p. 59 |
Osman Demirhan, Deniz Tastemir, Ramazan Günesacar, Ali Irfan Güzel, Davut Alptekin
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86176 PMID:22090714Background: Mannose-binding lectin gene 2 (MBL2) plays a very important role in the first line of host immune response in Down syndrome (DS). The importance of MBL2 gene polymorphisms in children with DS is unclear, and no research has addressed MBL2 gene polymorphisms in patients with DS. This is the first report describing an important association between MBL2 gene polymorphisms and infections in children with DS.
Materials and Methods: We compared the frequency of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) at two codons of the MBL2 gene in a cross sectional cohort of 166 children with DS and 229 controls. Polymorphisms at codons 54 (GGC→GAC) and 57 (GGA→GAA) in exon 1 of the MBL2 gene were typed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) technique using the restriction enzymes BshN1 (derivated from Bacillus sphaericus) and MboII (derivated from Moraxella bovis), respectively.
Results: MBL2 codon 54 GA genotype frequency was found to be lower in patients with DS (22.9%) than those of healthy controls (35.8%), differences were statistically significant (OR = 0.532, 95% CI = 0.339-0.836, P = 0.008). On the other hand, codon 57 polymorphism in the MBL2 gene was detected in none of the DS patients, but only one person in the control group showed codon 57 GA genotype (OR = 1.004, 95% CI = 0.996-1.013, P = 1.000).
Conclusion : Our data provides an evidence for the first time that a homozygote or heterozygote for the variant, MBL2 alleles, is not associated with infections in patients with DS, and do not influence the incidence of infections. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
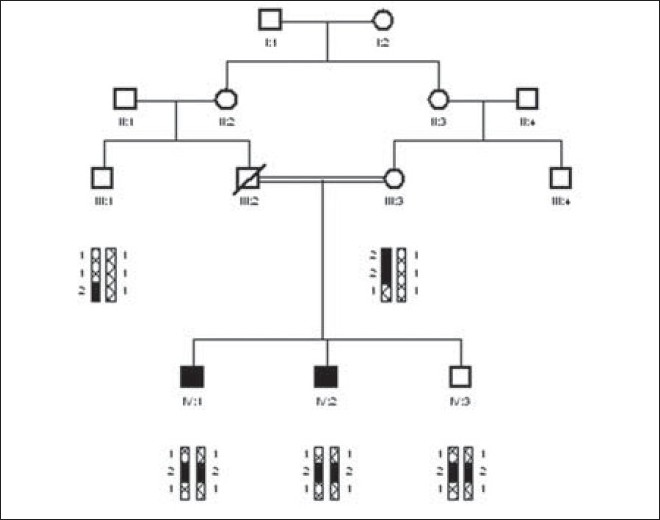  |
Molecular investigation of mental retardation locus gene PRSS12 by linkage analysis |
p. 65 |
Zafar Ali, Masroor Ellahi Babar, Jamil Ahmad, Muhammad Zubair Yousaf, Muhammad Asif, Sajjad Ali Shah
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86178 PMID:22090715The present study was carried out to determine the prevalence of families having mental retardation in Pakistani population. We enrolled seven mentally retarded (MR) families with two or more affected individuals. Family history was taken to minimize the chances of other abnormalities. Pedigrees were drawn using the Cyrillic software (version 2.1). The structure of pedigrees shows that all the marriages are consanguineous and the families have recessive mode of inheritance. All the families were studied by linkage analysis to mental retardation locus (MRT1)/gene PRSS12. Three STR markers (D4S191, D4S2392, and D4S3024) in vicinity of mental retardation (MR) locus (MRT1)/gene PRSS12 were amplified on all the sample of each family by PCR. The PCR products were then genotyped on non denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). The Haplotype were constructed to determine the pattern of inheritance and also to determine that a family was linked or unlinked to gene PRSS12. One out of the seven families was potentially linked to gene PRSS12, while the other six families remain unlinked. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
  |
Novel mutations in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy from Indian population |
p. 70 |
Pranathi Rao Pamuru, D V.N Maithili, Khalid Mohiuddin, Narasimhan Calambur, Pratibha Nallari
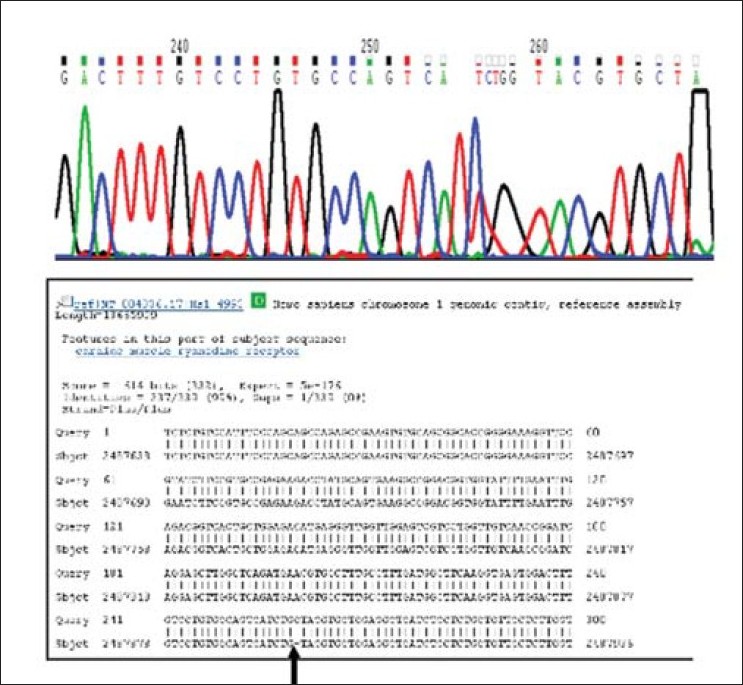
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86182 PMID:22090716Background: Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) is a progressive condition with right ventricular myocardium being replaced by fibro-fatty tissue. The spectrum of the expression may range from benign palpitations to the most malignant sudden death. Most of the mutations identified for the condition are localized in desmosomal proteins although three other nondesmosomal genes (cardiac ryanodine receptor-2, TGF-b3, and TMEM43) have also been implicated in ARVC. Both desmosomal and nondesmosomal genes were screened in a set of patients from local population.
Materials and Methods: A set of 34 patients from local population were included in this study. Diagnosis was based on the criteria proposed by task force of European Society of Cardiology/International Society and Federation of Cardiology. Polymerase chain reaction-based single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis was carried out, and samples with abnormal band pattern were commercially sequenced.
Results : Screening of cardiac ryanodine receptor revealed an insertion of a base in the intronic region of exon-28 in a patient, leading to a creation of a cryptic splice site. Screening of plakohilin-2 for mutations revealed an abnormal band pattern in three patients. Two of them had similar abnormal band pattern for exon-3.1. Sequencing revealed a novel 2 base pair deletion (433_434 delCT), which would lead to premature truncation of the protein (L145EfsX8). Another patient showed abnormal band pattern for exon-3.2 and sequencing revealed a missense mutation C792T leading to amino acid change P244L, in N-terminal, and this substitution may cause disturbances in the various protein-protein interactions.
Conclusion : This study reports novel cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR-2) mutations and Pkp-2 for the first time from Indian population. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (4) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
  |
Cytoprotective effect of honey against chromosomal breakage in fanconi anemia patients in vitro |
p. 77 |
Faeza Abdel Mogib El-Dahtory, Sohier Yahia
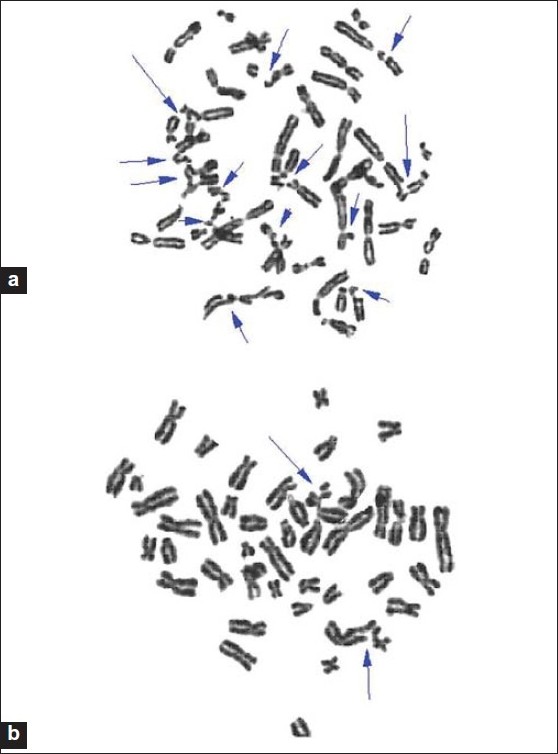
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86184 PMID:22090717Background : Natural honey is widely used all over the world as a complementary and alternative medicine in various disorders including Fanconi anemia (FA). FA is a rare genetic chromosomal instability syndrome caused by impairment of DNA repair and reactive oxygen species (ROS) imbalance. This disease is also related to bone marrow failure and cancer. The aim of this study was to evaluate the cytoprotective effect of honey on mitomycin C (MMC-) induced chromosomal damage in peripheral lymphocytes from FA patients.
Materials and Methods :Treatment of these complications with alkylation agents MMC may enhance chromosomal breakage. We have evaluated the effect of honey on MMC- induced chromosomal breakage in FA blood cells using chromosomal breakage assay. The basal chromosomal breakage count was higher among FA patients than healthy subjects.
Results : The addition of MMC alone gave a significantly higher of chromosomal breakage in FA patients than control group (P < 0.0001). Pre- treatment with honey significantly inhibited breakage induced by MMC in FA patients by its antioxidant effect.
Conclusion : Honey can prevent MMC- induced chromosomal breakage by its antioxidant effect. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chromosomal abnormalities as a cause of recurrent abortions in Egypt |
p. 82 |
Faeza Abdel Mogib El-Dahtory
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86186 PMID:22090718Background: In 4%-8% of couples with recurrent abortion, at least one of the partners has chromosomal abnormality. Most spontaneous miscarriages which happen in the first and second trimesters are caused by chromosomal abnormalities. These chromosomal abnormalities may be either numerical or structural.
Material and Methods : Cytogenetic study was done for 73 Egyptian couples who presented with recurrent abortion at Genetic Unit of Children Hospital, Mansoura University.
Results : We found that the frequency of chromosomal abnormalities was not significantly different from that reported worldwide. Chromosomal abnormalities were detected in 9 (6.1%) of 73 couples. Seven of chromosomal abnormalities were structural and two of them were numerical.
Conclusion : Our results showed that 6.1% of the couples with recurrent abortion had chromosomal abnormalities, with no other abnormalities. We suggest that it is necessary to perform cytogenetic in vestigation for couples who have recurrent abortion. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| BRIEF REPORTS |
 |
|
|
  |
Association of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 gene single nucleotide polymorphism with type 1 diabetes mellitus in Madurai population of Southern India |
p. 85 |
Beatrice Philip, W Isabel
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86189 PMID:22090719Type 1 diabetes mellitus formerly called juvenile diabetes, is an organ specific T-cell mediated autoimmune disease characterized by the progressive loss of function of the insulin producing beta-cells of the islets of Langerhans. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 gene (CTLA-4) has been proposed as a candidate gene for conferring susceptibility to autoimmunity. Association of CTLA-4 gene polymorphism is well established in autoimmune endocrinopathies across world population. The present study was conducted to investigate the association of CTLA-4 exon 1 49A/G polymorphism with TIDM in Madurai, a city in Southern India. Fifty three clinically proven T1DM patients and 53 control subjects with no history of autoimmune disease were recruited for the study. Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood. CTLA-4 exon 1 49 A/G polymorphism was assessed using PCR-RFLP methods. Our findings revealed a significant association of CTLA-4 exon 1 49 A/G polymorphism with T1DM in Madurai population. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (7) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
  |
G-C heterozygosis in mutS homolog2 as a risk factor to hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer in the absence of a family medical history |
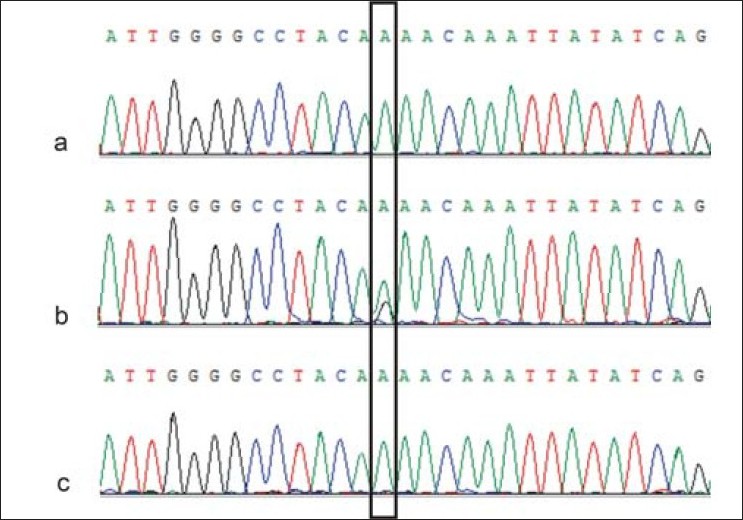
p. 90 |
Jorge Alfonso Arvayo-Zatarain, José Manuel Grijalva-Chon, Reina Castro-Longoria, Alejandro Varela-Romero
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86191 PMID:22090720To detect the presence of point mutations in a small section of the mutS homolog2 (MSH2) gene in both healthy and affected persons treated at the General Hospital of the State of Sonora, a 353 base pair section of the MSH2 gene was amplified and sequenced from six persons affected by hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer and from 19 healthy persons. The affected persons did not show the mutations reported in the scientific literature; however, six healthy persons were heterozygote and mutant-allele carriers. The heterozygote condition implies that carriers are candidates for the development of colorectal cancer. However, it is important to know the family medical history when investigating hereditary mutations. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| CASE REPORTS |
 |
|
|
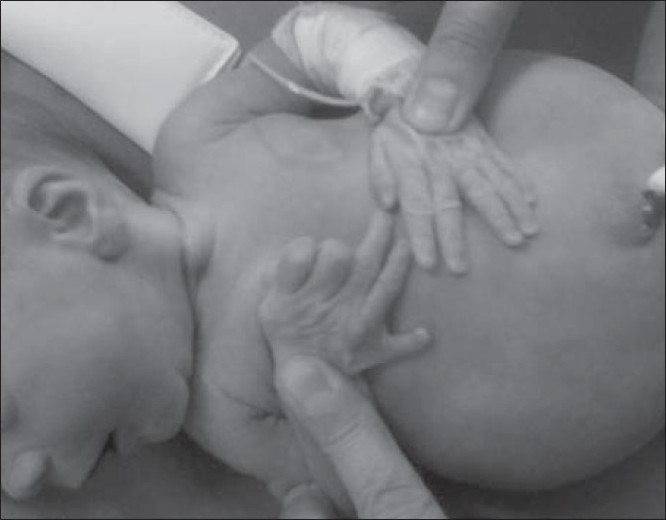  |
McKusick-Kaufman or Bardet-Biedl syndrome? A new borderline case in an Italian nonconsanguineous healthy family |
p. 94 |
Massimiliano Chetta, Nenad Bukvic, Valeria Bafunno, Michelina Sarno, Rosario Magaldi, Gianpaolo Grilli, Vincenzo Bertozzi, Francesco Perfetto, Maurizio Margaglione
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86194 PMID:22090721McKusick-Kaufman syndrome (MKS, OMIM #236700) is a rare syndrome inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern with a phenotypic triad comprising hydrometrocolpos (HMC), postaxial polydactyly (PAP), and congenital cardiac disease (CHD). The syndrome is caused by mutations in the MKKS gene mapped onto chromosome 20p12 between D20S162 and D20S894 markers. Mutations in the same gene causes Bardet-Biedl-6 syndrome (BBS-6, OMIM #209900) inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. BBS-6 comprises retinitis pigmentosa, polydactyly, obesity, mental retardation, renal and genital anomalies. HMC, CHD, and PAP defects can also occur in BBS-6, and there is a significant clinical overlap between MKS and BBS-6 in childhood. We describe a new borderline case of MKS and BBS syndrome and suggest insights for understanding correlation between MKKS gene mutations and clinical phenotype. Here, we report the results of molecular analysis of MKKS in a female proband born in an Italian nonconsanguineous healthy family that presents HMC and PAP. The mutational screening revealed the presence of two different heterozygous missense variants (p.242A>S in exon 3, p.339 I>V in exon 4) in the MKKS gene, and a nucleotide variation in 5'UTR region in exon 2 (-417 A>C). |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (1) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
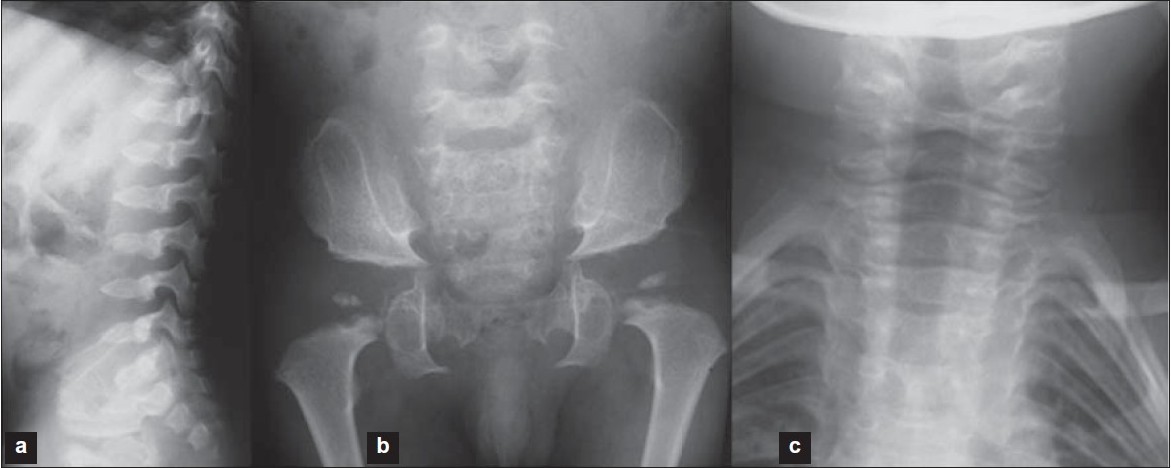  |
A recurrent mutation in Moroccan patients with Dyggve-Melchior-Clausen syndrome: Report of a new case and review |
p. 97 |
Siham Chafai Elalaoui, Tajir Mariam, Ratbi Ilham, Doubaj Yassamine, Sefiani Abdelaziz
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86197 PMID:22090722Dyggve-Melchior-Clausen (DMC) syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder. It is a spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia associated with mental retardation. Clinical manifestations include coarse facies, microcephaly, short trunk dwarfism, and mental retardation. Mutations in Dymeclin gene (DYM), mapped to chromosome 18q21.1, is responsible for DMC. We report here the observation of a consanguineous Moroccan patient having DMC syndrome. The molecular studies showed a previously reported homozygous mutation at c.1878delA of DYM gene. We discuss this recurrent mutation in Moroccan patients with DMC syndrome with a review. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
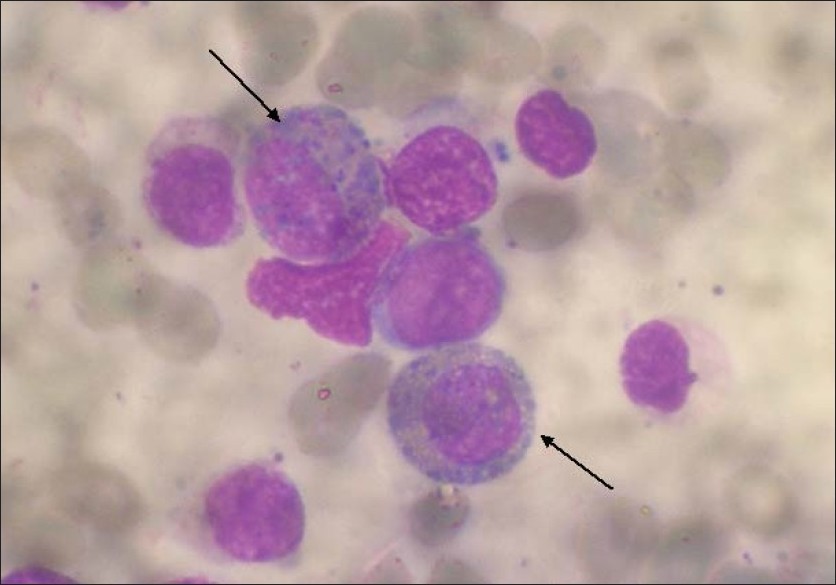  |
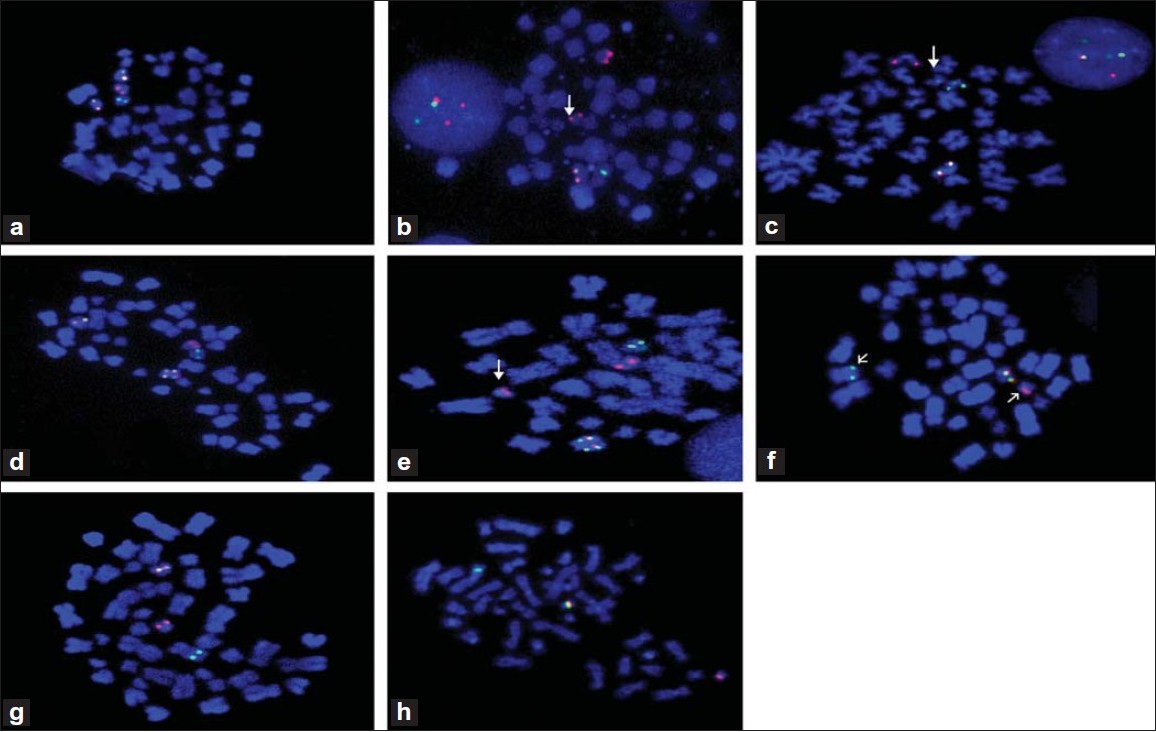
Deletion of ABL/BCR on der(9) associated with severe basophilia |
p. 100 |
Shantashri Vaidya, Manisha Madkaikar, Kanjaksha Ghosh, Babu Rao Vundinti
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86198 PMID:22090723Chronic basophilic leukemia is a rare form in chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Only limited number of reports are available. Herein, we describe a patient who presented with fatigue, weight loss, leucocytosis, prominent basophilia, and mild eosinophilia. On biopsy, bone marrow was hypercellular with marked basophils. The immunophenotype showed abnormal expression of CD7, which is suggestive of basophilic maturation. Chromosomal analysis from GTG-banded metaphases revealed Ph positivity, and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with BCR/ABL dual color, dual fusion probe showed single fusion on the der(22) chromosome and ABL/BCR fusion was deleted on the der(9) chromosome. The deletion (ABL/BCR) on der(9) may be associated with basophilia which may be also indicative of the transformation of CML to acute myeloid leukemia. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
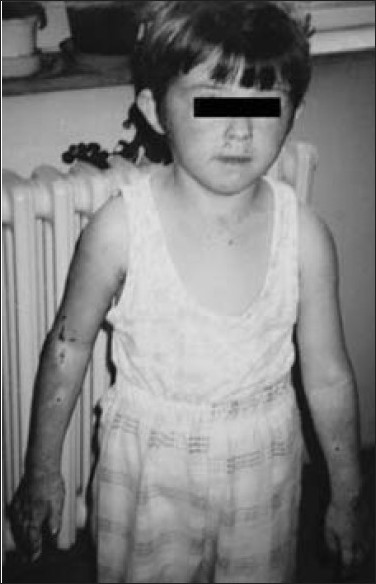  |
Congenital erythropoietic porphyria with two mutations of the uroporphyrinogen III synthase gene (Cys73Arg, Thr228Met) |
p. 104 |
Zoran Gucev, Nevenka Slavevska, Velibor Tasic, Nevenka Laban, Nada Pop-Jordanova, Dragan Danilovski, Jacqueline Woolf, Duncan Cole
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86199 PMID:22090724Congenital erythropoietic porphyria (CEP) is an autosomal recessive inborn error of metabolism that results from the markedly deficient activity of uroporphyrinogen III synthase (UROS). We describe a 14-year-old girl with red urine since infancy, progressive blistering and scarring of the skin, and moderate hemolytic anemia. After years of skin damage, her face is mutilated; she has a bald patch on the scalp, hypertrichosis of the neck, areas of skin darkening, and limited joint movements of the hands. Total urine excretion and fecal total porphyrin were both markedly raised above normal levels. Sequencing of the UROS gene identified two mutations causing CEP (Cys73Arg, Thr228Met). The patient lesions are progressing. Bone marrow transplantation and/or gene therapy are proposed as the next steps in her treatment. In brief, we describe a CEP with confirmed two pathogenic mutations, severe phenotype and discuss the various treatment options available. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
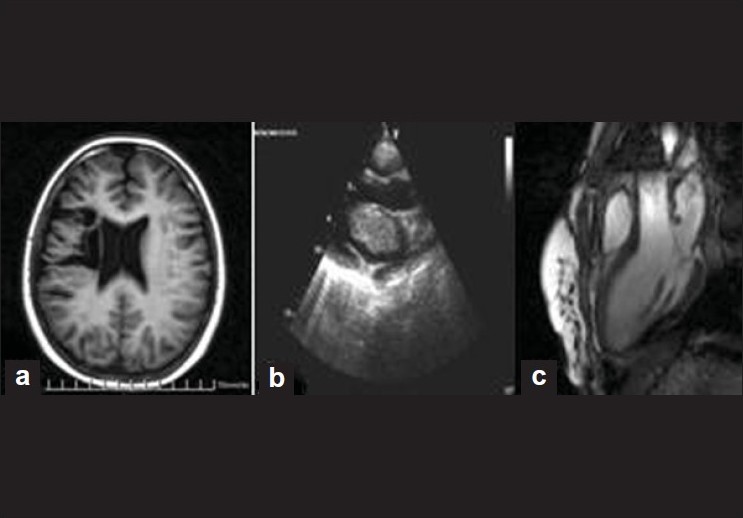  |
Early recurrent left atrial myxoma in a teenager with de novo mutation of Carney complex |
p. 108 |
Mila S Stajevic, Vladislav A Vukomanovic, Vladimir D Kuburovic, Slavisa M Djuricic
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86200 PMID:22090725We report a case of an extremely early recurrence of left atrial myxoma in a 13-year-old girl. On hospital admission, the clinical presentation was of cerebral embolism with noticeable spotty skin pigmentation and hypertelorism. The left atrial myxoma originated from the roof of the left atrium. The histology specimen showed typical finding of a myxoma. Six months later a new intracardial mass was evacuated, the postoperative result showing the same type of myxomatous tissue. Genetic investigations demonstrated Carney complex. The genetic analysis of the child's family was negative, demonstrating de novo mutation of this rare disorder. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (3) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|
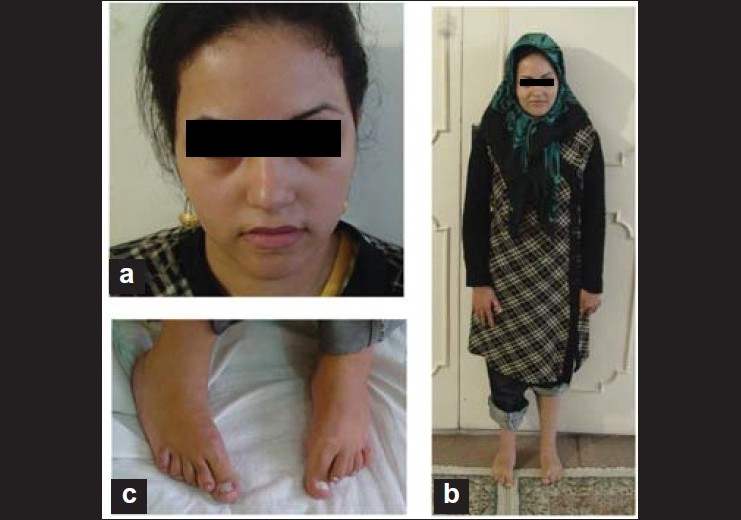  |
Prenatal diagnosis in a mentally retarded woman with mosaic ring chromosome 18 |
p. 111 |
Eiman Bagherizadeh, Farkhondeh Behjati, Seyed Hoseinali Saberi, Yousef Shafeghati
DOI:10.4103/0971-6866.86201 PMID:22090726We present a pregnant woman with mental retardation and mosaic for ring 18 referred for prenatal diagnosis. Major clinical features included short stature with clinodactyly in feet, foot deformity and club feet, hypotonia, kyphosis, and absence of breast development, low set ears, high arched palate, dental decay and speech disorder. Prenatal diagnosis was carried. Using amniocentesis. The fetus had a normal karyotype described as 46,XX. The fetus was evaluated for clinical features after delivery; she was healthy with no abnormal clinical characterizations. |
| [ABSTRACT] [HTML Full text] [PDF] [Mobile Full text] [EPub] [Citations (2) ] [PubMed] [Sword Plugin for Repository]Beta |
|
|
|
|
|